Environment
Comments: No Comments
Energy monitoring is a key first step in effective energy management, as it allows organizations to understand their energy consumption patterns and identify routine waste in the process. Reviewing utility bills is a basic initial action that can offer significant insights into how an organization consumes energy and what opportunities may exist for immediate and longer-term savings.
Uncovering Opportunities
Working with a Certified Energy Manager (CEM) to review and analyze a 12-month history of utility data for both electricity and natural gas can help identify peak demand, load profile, taxes, and historic trends in usage. This information can be used, in turn, to calculate savings on efficiency measures and projects based on utility costs. Such opportunities may include the following:
Tariff Review
A utility tariff governs how an energy provider (electric or natural gas) charges the customer for their electricity and natural gas usage. Utilities set out the rates, terms, and conditions of service in these tariffs. Electricity tariffs can vary widely by location and provider, hence the importance of reviewing the organization’s current tariff with its energy provider.
After reviewing utility bills and preparing a profile of energy usage, it is possible to compare the current tariff with other available tariffs to determine if there is a more cost-effective way to purchase energy. The utility may conduct these tariff reviews on your behalf; however, a second opinion can often identify savings opportunities to take advantage of the way a tariff may be structured. For example, a portion of the total utility bill is typically determined by actual demand and structure of the tariff. Where demand charges are nearing 50% of the bill, there are often opportunities for cost savings, including:
- Shifting production to take advantage of lower rates in off-peak hours or seasons.
- Staggering startups to reduce instantaneous demand.
Tax Exemption
If you are paying the full taxes on your electricity and natural gas, your organization may be eligible for a tax exemption depending on where the facility is located. The tax exemption typically applies to energy (gas or electric) that is used to manufacture saleable goods. Tax exemptions often apply to 75% to 99% of the facility’s total utility tax burden.
To receive the exemption, an energy tax study is required to determine how much energy at the facility is used in the manufacture of saleable goods (i.e., any processes that modify the product) versus the energy used for ancillary operation (e.g., warehousing, welfare spaces, lighting). Typically, these studies must be renewed when significant changes occur at the facility to impact load or every three years, whichever is soonest (depending on state-specific rules). The value of the tax emption can vary greatly depending on facility size.
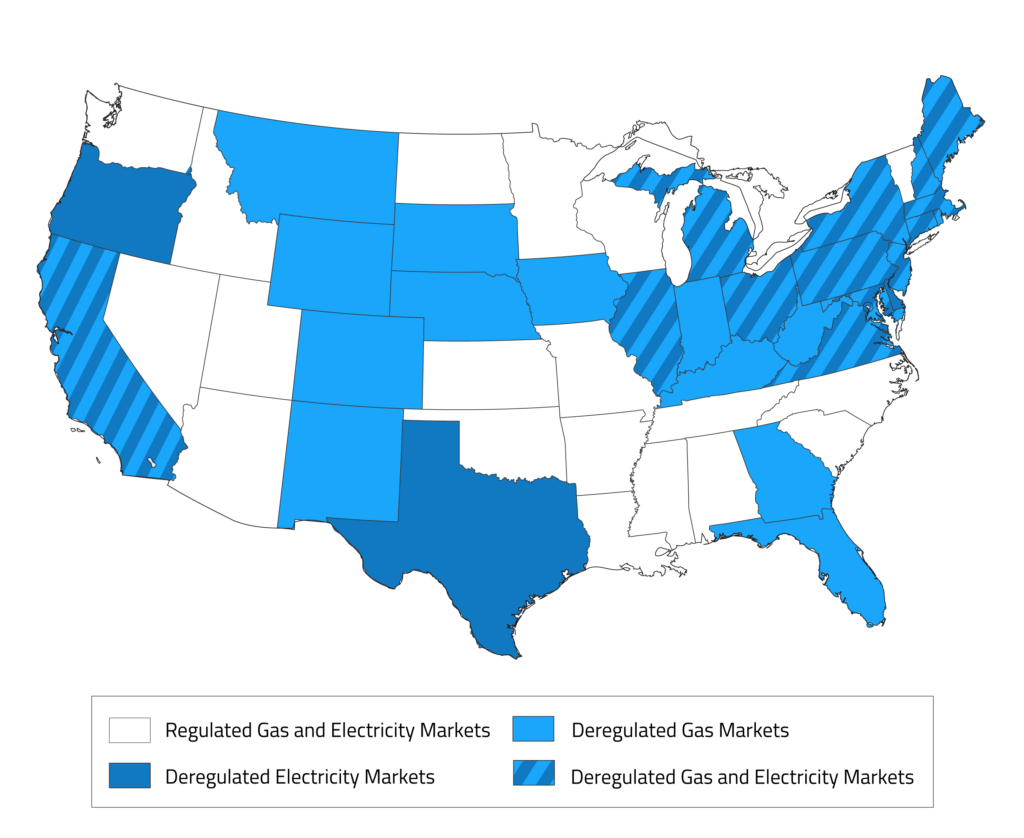
Energy Costs in the Open Market
Energy costs (gas and electric) can be compared against known market rates to determine whether there may be an opportunity for cheaper supply on the open market. The map below shows which states have a deregulated energy market. Any operations in these states may be able to find partnerships with third-party energy suppliers for cost savings.
Utility bills are just a starting point. The more data that can be reviewed and analyzed—and the more detailed it is—the easier it is to identify cost- and energy-saving opportunities within operations.
KTL has experience reviewing utility bills and helping organizations of all sizes identify energy consumption patterns and energy efficiency solutions. Please contact us for assistance in meeting your energy, environmental, and sustainability objectives.