
Getting to the Root Cause
At the most basic level, a root cause is the fundamental reason—or the highest-level cause—for the occurrence of a problem, incident, or event. The root cause sets in motion the entire cause-and-effect reaction that ultimately leads to the problem. Getting to the root cause of any problem is important not just for resolving the issue at hand, but for identifying underlying issues to ensure that similar problems do not occur in the future. This starts with a process called the root cause analysis (RCA).
What Is the Root Cause Analysis (RCA)?
A root cause can be permanently eliminated through process improvement. RCA is a method of problem-solving used to identify the underlying (i.e., root) cause(s) of a problem/incident. RCA can be used to solve problems and provide preventive actions for:
- Major accidents
- Everyday incidents
- Minor near misses
- Human errors
- Maintenance problems
- Medical mistakes
- Productivity issues
- Manufacturing mistakes
- Environmental releases
- Risk analysis, risk mapping
RCA is a systematic process based on the basic idea that effective management requires more than merely putting out fires. RCA focuses on finding a way to prevent these fires from recurring. Rather than just treating symptoms, RCA seeks to identify and address the true, underlying concerns that contribute to a problem or event.
Why is this important? If you just treat the symptoms of the problem, that alleviates them for the short term, but it does nothing to prevent the problem from coming back again. Lasting solutions address the underlying factors—the root cause(s)— that create the problem in the first place. Targeting corrective measures at the identified root causes, subsequently, is the best way to alleviate risk and ensure that similar problems do not occur in the future.
Best Practice
Both the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) encourage organizations to conduct RCA following an incident or near miss at a facility. In fact, facilities covered by OSHA’s Process Safety Management (PSM) standard are required to investigate incidents that resulted in (or could have reasonably resulted in) a catastrophic release of highly hazardous chemicals. Similarly, EPA’s Risk Management Program (RMP) regulations require regulated facilities to conduct incident investigations. In addition, certain management systems, including ISO and Responsible Distribution (National Association of Chemical Distributors) to name just a few, also require RCA.
Whether an organization is subject to PSM, RMP, or management system standards, identifying the root cause of any incident or problem through RCA is a best practice that can significantly benefit organizations by identifying underlying issues to ensure that similar problems do not occur in the future. So, how do you effectively implement RCA?
Six-Step Process
RCA can be broken down into a simple six-step process, as outlined below.
Step 1: Identify and Clearly Describe the Problem
The first step is to understand and document the problem/issue/incident that actually occurred. This might involve interviewing key staff, reviewing security footage, investigating the site, etc. to get an accurate account of the issue. Certainly safety- or security-related incidents might require an immediate fix or prompt action before the carrying out the complete RCA. This is always the first priority.
Some problems are easier to define than others based on what happened and the extent of the issue. When defining and describing the problem, it is important to be as descriptive as possible, as this will aid in future steps to identify the root cause(s).
For example, the first description below is somewhat vague. The second description provides an additional level of detail that more fully documents the situation:
- A forklift driver wasn’t wearing his seatbelt. (vague)
- During a walkthrough of the warehouse on 2/1/20, it was observed that forklift driver John Smith, who is a contract employee, was not wearing his seatbelt while operating the forklift. (clear)
Step 2: Identify Possible Causes…Why?
There are several methods for identifying possible root causes. One of the most common is known as the “5 Why Method”. This approach simply involves asking the question “Why” enough times (i.e., five times) until you get past all the symptoms of a problem and down to the underlying root cause of the issue. The detailed problem description put together during Step 1 serves as the starting point for asking “Why”.
Let’s take our problem description from above a step further to identify the possible causes using the 5 Why Method.
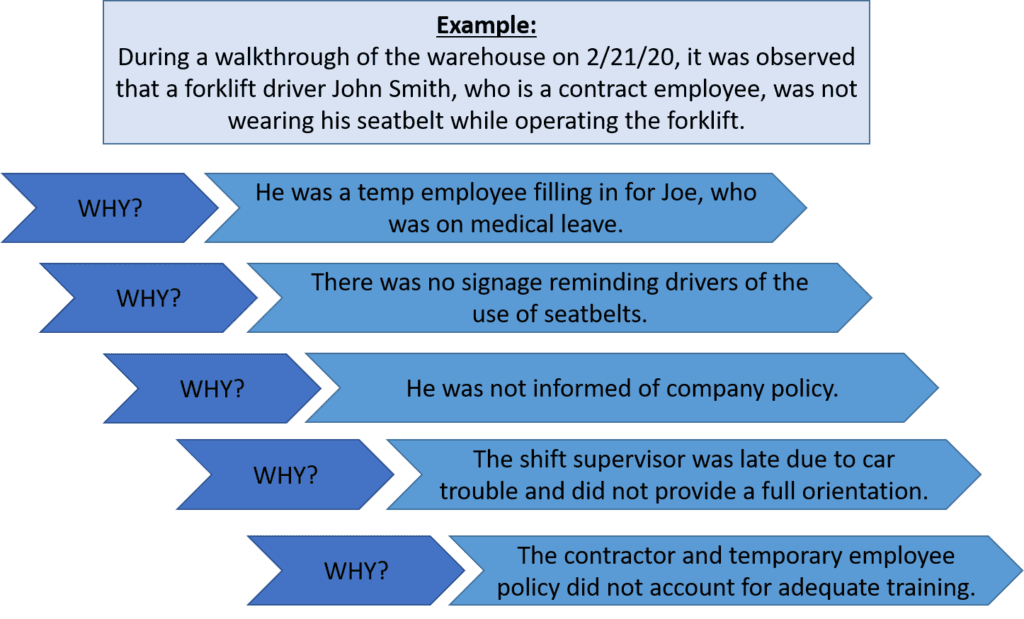 Step 3: Identify Root Cause(s)
Step 3: Identify Root Cause(s)
At this point, the 5 Why Method is leading you to the core issue that set in motion the entire cause-and-effect reaction and, ultimately, that led to the identified problem(s). It’s now time to determine whether the five whys have dug deep enough. Where does your questioning lead you? Is there one root cause or are there a series of root causes contributing to this incident? Often, there are multiple root causes that may be factors to address when preventing future incidents.
In our forklift operator case, the 5 Why Method points to the lack of a standardized checklist of all items to be trained on—including forklift training—prior to a new contract employee coming onsite.
Step 4: Corrective and/or Preventive Action Taken
Based on the identified root causes, it then becomes possible for the facility to determine what corrective and/or prevention actions (CAPAs) can be taken to fix the problem and, just as important, prevent it from occurring in the future. For our example, there are a number of potential CAPAs:
- Stop the employee from operating the forklift and educate him on seatbelt policy prior to resuming work
- Review contract/temp employee training program
- Retrain shift managers on training expectations
- Obtain training records for contract/temp employees
- Provide refresher/retraining, as necessary
- Add signage to forklifts and warehouse bulletin boards about seatbelt policy
Step 5: Analyze Effectiveness
The effectiveness of whatever action is taken in step 4 needs to be evaluated to determine whether it will resolve the root cause. If not, another CAPA should be explored, implemented, and analyzed to assess its impact on the issue/problem. If it is a root cause, it should help to resolve the issue and you should move on to step 6 below.
Let’s return to our example. You might ask, “Was the retraining effective?” An evaluation shows the following:
- Yes, the employee continues to operate the forklift using seatbelt.
- Yes, subsequent walkthroughs of the warehouse over the next six months have not resulted in any additional seatbelt violations.
- The next contract/temp employee brought on to assist during the busy end-of-year season was required to produce current training.
Step 6: Update Procedures, as necessary
As CAPAs are implemented, once they prove effective, related policies and procedures must be updated to reflect any changes made. This step ensures the outcomes of the RCA will be integrated into operations and used to prevent similar incidents from happening in the future.
In our current example, this might mean that the Contractor Policy is updated to include a new section specific to the hiring of contract/temp employees with the following requirements:
- Obtain valid training certificates for work performed
- Ensure Managers conduct on-the-job training for contract/temp employees specific to work performed
Benefits of RCA
Following these six steps will help to ensure a thorough investigation that identifies the root cause(s) versus just symptoms is conducted. It further ensures that any changes related to the root cause are integrated into the organization to prevent similar events from happening again. In the end, the RCA process can help:
- Reduce the risk of injury and/or death to workers and community members
- Reduce the potential for environmental damage
- Avoid unnecessary costs resulting from business interruption; emergency response and cleanup; increased regulation, audits, and inspections; and OSHA or EPA fines
- Improve public trust by maintaining an incident-free record
- More effectively control hazards, improve process reliability, increase revenues, decrease production costs, lower maintenance costs, and lower insurance premiums

Employees Need Rules, Not Regulations
KTL recently announced our partnership with Martin Mantz Compliance Solutions (Martin Mantz), developer of the GEORG Compliance Management System® software. KTL is providing regulatory compliance expertise to the German-based company as it expands its offerings to clients with operations in the United States.
In this recent article, our partners at Martin Mantz discuss how Rudolph Logistics Group, an international logistics service provider from Germany, is using GEORG as a compliance solution to provide employees clear information in accordance with ISO standards on:
- Tasks – what they have to do
- Responsibilities for implementation – who needs to do it
- Date/time of completion – when it needs to be done
- Description of the way the task is to be performed – how the task must be fulfilled
The objective is to simplify requirements to the extent possible so employees can focus on tasks to be completed without needing to interpret complicated and extensive guidelines. Read more…

Comments: No Comments
KTL Announces Partnership with German Company Martin Mantz
KTL is pleased to announce our partnership with Martin Mantz Compliance Solutions (Martin Mantz), developer of the GEORG Compliance Management System® software. KTL is providing regulatory compliance expertise to the German-based company as it expands its offerings to clients with operations in the United States.
“Martin Mantz has created something unique with the GEORG software in that it simplifies and provides an interpretation of legal and technical requirements in a customer-specific database,” KTL Principal Lisa Langdon states. “KTL’s understanding of industrial operations, as well as U.S. legal and technical requirements (e.g., EPA, OSHA, FDA, ISO), allows us to translate these requirements into simple tasks in the GEORG system that employees can follow to help fulfill regulatory requirements.”
How GEORG Works
GEORG is used to make the requirements of standards and regulations comprehensible and transparent. KTL specializes in the practical mapping of legal requirements and audits. These audits allow KTL to create technical content for the GEORG system based on facility-specific applicability. We then work directly with the company to delegate the identified tasks. If there are revisions in the standards/regulations, KTL works in the system to ensure tasks are updated to meet regulatory requirements.
The benefits of this approach include:
- Effectiveness – All tasks are assigned, easily formulated, and regularly updated.
- Efficiency – The effort and expertise required to understand complicated regulations is reduced.
- Transparency – Responsibilities are clear and easily visible to all employees.
- Conformity – Compliance status within the system reflects the degree of fulfilment of the related requirements.
Faber-Castell Expands GEORG Implementation to U.S. Subsidiary
Faber-Castell Cosmetics, an internationally renowned Martin Mantz customer with worldwide operations, is already benefitting from the Martin Mantz-KTL partnership. After successful implementation of the GEORG software in their German facilities, Martin Mantz has worked with KTL to expand usage to Faber-Castell’s subsidiary in the U.S.
About Martin Mantz Compliance Solutions
Martin Mantz Compliance Solutions, based in Grosswallstadt and Leipzig, Germany, offers its contractual partners services in the area of legal organization (GEORG) of companies to avoid organizational negligence and compliance violations. This includes consulting and provision of the compliance software GEORG Compliance Management System®, implementation of the technical and legal modules, as well as construction and maintenance of the customer-specific database. https://www.martin-mantz.de/
About Kestrel Tellevate LLC
KTL is a multidisciplinary consulting firm that specializes in providing environmental, health, and safety (EHS) and food safety management and compliance consulting services to private and government clients. Our primary focus is to build strong, long-term client partnerships and provide tailored solutions to address regulatory requirements. KTL’s services include management system development and implementation, auditing and assessments, regulatory compliance assistance, information management solutions, and training. KTL is a Small Business Administration-registered company with headquarters in Madison, WI and Atlanta, GA and offices across the Midwest and Washington, D.C. www.kestreltellevate.com

Principles of Auditing
To ensure companies uphold standards (internal or external) and continuously improve performance, audits are critical. In short, there are three primary purposes of auditing:
- Verify conformance with the standard/requirement – Are we doing what the standard/requirement says we must do?
- Verify implementation of stated procedures – Are we following the steps in our documented procedures?
- Evaluate effectiveness – Are we accomplishing our goals and objectives?
For an audit to be effective, appropriate mechanics must be in place when it comes to planning, execution, and reporting.
PLANNING
As with most things, your execution will only be as good as your plan. All good audits must begin with planning. This involves everything from planning for your team, to planning out the scope of the audit, to planning all the associated logistics.
Auditors: Who Is on the Team?
Depending on the size and complexity of the audits, audit teams need to be selected. These individuals must be independent of the area being audited and trained in the basic elements of the facility’s management system and/or programs. Team members will be led by a trained auditor. The auditor’s responsibilities include the following:
- Comply with and communicate audit requirements
- Prepare working documents under the direction of the Lead Auditor
- Plan and carry out the assigned responsibilities within the scope of the audit
- Collect and analyze evidence to draw conclusions
- Document audit observations and findings
- Report audit results to Lead Auditor
- Retain and safeguard audit documents
- Cooperate with and support the Lead Auditor
- Assist in writing the report
As indicated above, one person on the team is typically designated the Lead Auditor. This individual will coordinate audit assignments and address any questions/concerns that may arise. Specifically, the Lead Auditor has the following responsibilities:
- Assigns team members specific management system/program elements, functions, or activities to audit
- Provides instructions on the audit procedure to follow
- Makes changes to work assignments, as necessary, to ensure the achievement of audit objectives
Audit Objectives, Scope, and Plans: What Are We Auditing?
The audit is all about:
- Conformance – auditing sections of the standard/requirements to determine if the system conforms
- Implementation – auditing work instructions to see if they are being followed
In determining the audit scope, it is importation to define what is to be audited (e.g., policy, planning, implementation, checking/corrective action, management review). If the organization has more than one physical location, the scope may outline what physical locations and/or organizational activities are to be audited (e.g., production lines or departments). These factors will ultimately also help determine the length of the audit.
Logistics: How Are We Going to Do This?
There are many things to factor into the audit from a logistical standpoint for it to go smoothly. Safety should always be of utmost concern. What precautions do auditors need to take? Is there any PPE that might be necessary? Do auditors need any special safety training introduction or training before conducting the audit? Consider the facility. Auditors need to understand the operation/activity being audited. In line with this, the auditor must also have an understanding of whether there is any equipment or special resources needed, ranging from technical support (e.g., tablets, smartphones) to lunch. Finally, it is important to make sure there are no conflicts of interest when it comes to the auditor and the facility that is being audited.
EXECUTION
Once planned appropriately, audits should be conducted according to the program elements. Interviews and objectives evidence will both provide the support needed to conduct a valid audit.
Program Elements
The auditor must know in advance which elements are being covered in an audit so he/she can:
- Control the pace of the audit.
- Guide the course of the audit.
That being said, additional audit activities should not be restricted if other issues arise.
Auditing should only be done against current controlled work instructions or procedures related to the program elements. Procedures that are being used in the field must be verified. Historical and/or uncontrolled procedures should not be used.
Auditors must remember that they are creating a record. Notes should include statements, document numbers, identifiers (e.g., department, area), positions. Common pitfalls to be avoided in taking notes include abbreviations, no location identifier for observations, no document references, illegible, pejorative, cryptic. These things all impact the credibility of the audit.
Interviews
The goal of an interview in the audit is to obtain valid information. However, how questions are asked will impact the answer. Auditors must prepare and know what questions need to be asked and how to ask them in advance of the audit. Creating an atmosphere of trust and open communication is key to getting open and honest responses. Remember, the goal is to audit the system, not the interviewee.
The following are good rules of thumb for conducting effective audit interviews:
- Direct questions to the person who does the job, not to the supervisor.
- Never talk down to anyone.
- Speak the person’s language.
- Speak clearly and carefully.
- LISTEN!
- Use who, what, where, when and why in your questioning vs. can or does.
Objective Evidence
Objective evidence provides verifiable information, records, or statements of fact. This is vital in any audit report. Objective evidence can be based on any of the following:
- Interviews
- Examination of documents
- Observation of activities and conditions
- Results of measurements
- Tests
- Other means within the scope of the audit
Evidence should be firsthand evidence based on witnessed fact, not supposition, presumption, hearsay, rumor, or conjecture. It can be qualitative or quantitative, but it should be repeatable.
REPORTING
Findings form the basis of the report. Findings can be classified in one of two ways:
- Nonconformance is the observed absence of or lapse in a required procedure or the total breakdown of a procedure that can cause a negative impact on the organization’s environmental performance. These can fall into a few categories:
- Does not meet the requirements of the standard. This may include issues identified with records, procedures, work instructions, and use of controlled documents.
- Is not fully implemented. Most commonly, these implementation nonconformances may relate to training, communication, and documentation.
- Is improperly implemented. This is often demonstrated by worker lack of understanding, improper implementation of written work instruction, or missing stated required deadlines.
- Opportunity for improvement is just that—an opportunity to improve management to either reduce impacts, minimize legal requirements, prevent future nonconformances, or improve business performance.
The following examples and tips can serve as guidelines for writing useful and more concrete findings that will the company to identify opportunities for improvement:
- Do not overstate conclusions.
- Poor: The procedure for handling spent light bulbs is being ignored.
- Better: Three spent fluorescent bulbs were found in the general trash.
- State the problem clearly and exactly.
- Poor: Instruments are not being calibrated.
- Better: The sampling and analytical instruments in the wastewater treatment plant are not calibrated.
- Avoid generalities.
- Poor: The area’s empty drum management process is inadequate.
- Better: The hi-lo driver in the area handling empty drums was not trained on hazardous material handling.
- Communicate the extent of the problem fully.
- Poor: All cardboard in the catalytic converter area is being sent to the compactor.
- Better: None of the cardboard in the catalytic converter area was being stored and/or evaluated for reuse as dunnage.
- Do not focus on criticisms of individuals.
- Poor: Jim Jones had no understanding of the safety policy.
- Better: Discussions with several employees indicated that the safety policy was not fully understood.
- Give specific references.
- Poor: Hazardous waste area inspections have not been conducted.
- Better: Weekly hazardous waste storage area inspections (VMEWP-008) have not been conducted since June 2002.
- Avoid indirect expressions.
- Poor: There were occasions when the reports were not filed on time. It appears the air monitoring equipment is not calibrated.
- Better: Reports were filed late on ten occasions in 2002. There were no records of air monitoring equipment calibrations for 2001 or 2002.
Audits are a skilled activity. They provide the basis for assessment of conformance and, correspondingly, company actions to improve performance. For audits to be valuable, however, the audit process must be consistent and controlled. Clearly and correctly documented nonconformances lead to appropriate corrective actions—the mechanism for translating audits into improvements.

4 Steps to Reporting Audit Results
The audit report communicates the information, findings and opinions derived from the audit. The report communicates either acceptability of the current status of the management system or reports non-conformances that need corrective action. The following outlines the suggested steps for reporting audit results.
Step 1. Assess the Status of Current Internal Controls
One of the auditor’s main responsibilities is to evaluate whether the current internal controls that govern the management system are adequate. Do the audits:
- Highlight areas of concern or hazards that may be a failure waiting to happen?
- Focus attention of the 20% of the factors that cause 80% of the problems?
- Help to eliminate ineffective controls or make existing controls better?
- Aid in the detection and prevention of deficiencies or non-conformances?
- Look through and investigate possible “homeblindness”?
- Verify the management system links are supportive and feed each other information to assure continual improvement?
The auditors must constantly challenge the status quo and push the management system forward beyond its comfort level.
Step 2. Prepare Audit Report
Most facilities use a formal audit report system. The audit report format is prescribed and followed by the auditor. The auditor typically states:
- Date and time of audit
- Department audited
- Management system clauses audited to
- Personnel interviewed
- Documents reviewed
- Summary of findings
- Conformance or non-conformance determination
Step 3. Discuss Audit Findings
The lead auditor will then take the completed audit report and review the contents with the affected department head. Upon acceptance by the department head, the final audit report should then be signed by the department head verifying acceptance and responsibility for any change(s) required.
Step 4. Determine Plan of Action
The entire reason for conducting internal management system audits is to verify conformance and continually improve on the management system. Therefore, it is extremely important that all identified non-conformances are corrected in a timely manner.
Some companies place all audited non-conformances into their corrective/preventive action process for tracking purposes. Others place only critical non-conformances into the corrective/preventive action process. Regardless of the mechanics of tracking the identified audited non-conformances, it is imperative that corrective action is taken.
Once the corrective action is in place, the auditors should review the actions taken and verify the root cause was identified properly and resolved. An accept or reject decision can then be rendered for the change action.
If acceptable, no further action is required, and the issue is considered resolved. If unacceptable, the department head must complete a new root cause analysis, develop a new action plan, and put the new action plan into place. The auditors will now review the new action plan and make a determination of acceptance or rejection.
Audit Team Members
It is advisable to rotate your internal management system audit team members. This will allow for fresh perspective and a new set of eyes to look at the management system. This serves many purposes:
- Gives a specific timeframe of responsibly for those thinking of enlisting as an auditor
- Allows for gradual increase of responsibility over time; new auditors learn and perform audits, older auditors become mentors for the new auditors, graduates leave program and are viewed by company personnel as “knowledge experts” on the management system
- Allows for fresh perspective on auditing
- Trains numerous employees on the management system
- Reinforces the concept of continuous improvement
Are You Prepared?
Use your answers to the questions below to evaluate your preparation for reporting audit results.
- Has the auditor evaluated the current internal controls for suitability, adequacy, and effectiveness?
- Does the auditor have hard copy evidence of conformance and/or non-conformance?
- Have all questions prepared prior to the audit been satisfactorily answered and explained?
- Is the audit report clear, concise, and informative?
- Does the department head agree or disagree with the findings?
- Are all identified non-conformances tracked and resolved in a timely manner?
- Based on audit non-conformances, are procedures and work instructions being changed and improved?
- Do employees understand the management system is being audited, not the employee?
- Is change readily accepted by company personnel?

Environment / Quality / Safety
Comments: No Comments
Partnering with Government Agencies to Manage Projects
From time to time, private businesses are faced with the prospect of partnering with a government agency, office, or department in order to accomplish a goal or undertake a project. Reasons vary: the effort may result from an enforcement action, consent order, or settlement agreement, or it may simply be a strategic priority that requires joining forces with a federal, state, or local government office. In any case, working with government agencies presents opportunities and challenges not regularly encountered in a competitive business’s projects.
Reset Your Clock
Government agencies do not move at the speed of competitive business—they typically move much slower. Government budgeting and spending are intentionally lengthy processes that are subject to the political winds. As a result, it is not unusual for agencies to employ (legacy) infrastructure and systems that have worked in the past, regardless of apparent inefficiencies today.
If the agency will be contributing financially to the effort, it may take years for funding to be proposed, studied, discussed, approved in a budget, and then approved to spend. Similarly, any decision-making can be an arduous and lengthy process involving a multitude of managers and influencers.
Understanding how funding and decisions are made and who needs to be involved is critical to managing the time element of projects. Often, the dominant motive for decision-making is protection of the status quo and personal job security, versus “let’s try something new and exciting”. Stakeholder management requires understanding, patience, and persistence.
Take the Lead
Business should expect to take the lead in project management. Most government agencies will advertise successful projects after they are completed, but will keep unproven or work-in-progress low key, pending successful results. Similarly, they will participate as directed in the work but do not usually want to be viewed as driving a public-private partnership, as even the appearance of an overly close relationship with a particular business can compromise the agency’s perceived objectivity. Finally, many public agencies do not have trained project managers on staff to lead such an effort, while a business may.
Find an Agency Champion
Successful execution of the project plan requires timely coordination and cooperation from the agency, and may involve a number of different departments or functions within it. For example, building a joint facility may involve facilities, IT, security, finance, law, and operations departments. In order to get the cooperation needed from the various departments, those staffs will expect someone in their direct chain of command to prioritize the project.
In competitive business, a Vice President acting as project sponsor may have all the authority he/she needs to expect and get cooperation across the property. But in a government agency, a Director or Section Chief over one of the areas may carry absolutely no authority in another department. Government agencies tend to be very silo-ed in their structures, not matrixed. It is important to find a sponsor far enough up the chain to cover all areas involved and to communicate his support of the project to all areas—even if he/she is not regularly directly involved in the project.
Build a Lasting Relationship
So often, the only time business and agencies interact is when one needs something from the other. This can lead to a strained relationship, characterized by avoidance or begrudging interactions. These are the same agencies, however, where a positive working relationship can result in a business competitive advantage. Working closely with these gatekeepers of the regulations and public trust in a non-confrontational setting can set the foundation for a new relationship built upon mutual understanding and achieving common goals.
Government employees fill a valuable role in society by providing services and protecting society. Besides understanding the current enforcement priorities, they interact with customers, competitors and even employees, and can provide valuable information or ideas for businesses to improve efficiencies or help direct the focus of current business efforts.
Case Study: Utility Environmental Management System (EMS)
Kestrel managed a project with an investor-owned utility to design and implement an Environmental Management System (EMS) at a coal-fired power plant. The result of a consent order from the state Natural Resources Department, both the utility and the agency were involved from design and implementation to final auditing and EMS acceptance by the agency. The project and the associated agency interactions brought the plant higher confidence in its environmental plans and operations, and gave local regulators a deeper understanding of the utility business and ownership of the plant’s path forward.
Takeaways
Working with a government agency to manage a project is different than working with a competitive business. However, doing so can be beneficial to achieving both parties’ objectives if the company knows how to successfully navigate the working relationship:
- Understand how government funding and decisions are made before project kickoff.
- Actively manage government stakeholders—expect to take the lead.
- Find a project sponsor with the authority to ensure cooperation from all agency departments involved.
- Take advantage of the opportunity to build a positive, long-lasting relationship.

Top 5 Critical Factors for Value-Added Auditing
Auditing is a management tool that can be used to evaluate and monitor the internal performance and compliance of your company with regulations and standards. An audit can also be used to determine the overall effectiveness of an existing system within your company.
How do you incorporate compliance auditing best practices to help maximize compliance, efficiency, and value of your audit? Here are five critical factors for value-added audits.
1. Goal Aligned with Business Strategy
There are many reasons why companies conduct audits:
- Support commitment to compliance
- Avoid penalties
- Meet management system requirements
- Meet corporate or customer mandates
- Support acquisition or divestiture
- Assess organizational structure and competency
- Identify cost saving and pollution prevention opportunities
- Determine alignment with strategic direction
It is vital to define and understand the goal of your compliance audit program before beginning the audit process. Establishing goals enables recognition of broader issues and can lead to long-term preventive programs. Not establishing a clear, concise goal can lead to a waste of resources.
Audit goals and objectives should be nested within the company business goals, key performance objectives, and values. An example of a goal might be to effectively measure environmental compliance while maintaining a reasonable return on investment.
Once the goal is established, it is important to communicate it across all functions of the organization to get company-wide support. Performance measurements should also be communicated and widely understood.
2. Management Buy-in
The audit program must have upper management support to be successful. Management must exhibit top-down expectations for program excellence, view audits as a tool to drive continuous improvement, and work to imbed audits within other improvement processes. Equally important, management must not use audit results to take punitive action against any person or department.
3. Documented Audit Program Systematically Applied
Describe and document the audit process for consistent, efficient, effective, and reliable application. Audit procedures should be tailored to the specific facility/operation being audited. A documented program will include the following:
- Scope. The scope discusses what areas/media/timeframe will be audited. The scope of the audit may be limited initially to what is manageable and can be done very well, thereby producing performance improvement and a wider understanding and acceptance of objectives. It may also be limited by identifying certain procedural or regulatory shifts and changes. As the program is developed and matures (e.g., management systems, company policy, operational integration), it can be expanded and, eventually, shift over time toward systems in place, prevention, efficiency, and best practices. It is important at the scoping stage to address your timeline. Audits should be scoped to make sure you get them done but also to make sure you have audited all compliance areas in an identified timeframe.
- Criteria. Compliance with requirements will clearly be covered in an audit, but what about other opportunities for improvement (e.g., pollution prevention, energy savings, carbon reduction)? All facilities need to be covered at the appropriate level, with emphasis based on potential compliance and business risks. Assess the program strengths, redundancy, integration within the organization, and alignment with the program goal. Develop specific and targeted protocols that are tailored to operational characteristics and based on applicable regulations and requirements for the facility. As protocols are updated, the ability to evaluate continuous improvement trends must be maintained.
- Auditor training (i.e., competency, bias). A significant portion of the audit program should be conducted by knowledgeable auditors (e.g., independent insiders, third parties, or a combination thereof) with clear independence from the operations being audited and from the direct chain of command. For organizational learning and to leverage compliance standards across facilities, it is good practice to vary at least one audit team member for each audit. Companies often enlist personnel from different facilities and with different expertise to audit other facilities. Periodic third-party audits further bring outside perspective and reduce tendencies toward “home-blindness”.
Training should be done throughout the entire organization, across all levels:
+ Auditors are trained on both technical matters and program procedures.
+ Management is trained on the overall program design, purpose, business impacts of findings, responsibilities, corrections, and improvements.
+ Line operations are trained on compliance procedures and company policy/systems.
Consider having auditor training conducted by an outside source to teach people how to decide what to audit and follow a trail. It can also work well to train internal auditors by having them audit alongside an experienced 3rd party.
- Audit conduct (i.e., positive approach). A positive approach and rationale for the audit must be embraced. Management establishes this tone and sets the expectation for cooperation among all employees. Communication before, during, and after the audit is vital in keeping things positive. It is important to stress the following:
- Auditor interviews are evaluating systems, not personal behaviors.
- The audit is an effective tool to improve performances.
- Results will not be used punitively.
- Audit reporting. Information from auditing (e.g., findings, patterns, trends, comparisons) and the status of corrective actions often are reported on compliance dashboards for management review. Audit reports should be issued in a predictable and timely manner. It is desirable to orient the audit program toward organizational learning and continual improvement, rather than a “gotcha” philosophy. “Open book” approaches help learning by letting facility managers know in advance what the audit protocols are and how the audits will be conducted. Documentation is essential, and reporting should always align with program goals and follow legal guidance. There is variability in what gets reported and how based on the company’s objects. For example:
- Findings only vs. opportunities for improvement and best management practices?
- Spreadsheet vs. long format report?
- Scoring vs. prioritization of findings (beware of the unintended consequences of scores!)?
- Recommendations for corrective actions included or left for separate discussion?
- Corrective and preventive action. Corrective actions require corporate review, top management-level attention, and management accountability for timely completion. A robust root cause analysis helps ensure not just correction/containment of the existing issue, but also preventive action to assure controls are in place to prevent the event from recurring. For example, if a drum is labeled incorrectly, the corrective action is to relabel that drum. A robust plan should be to also look for other drums that might be labeled incorrectly and to add and communicate an effective preventive action (e.g., training or posting signs showing a correctly labeled drum).
- Follow-up and frequency. Address repeat findings. Identify patterns and seek root cause analysis and sustainable corrections. Communications with management should be done routinely to discuss status, needs, performance, program improvements, and business impacts. Those accountable for performance need to be provided information as close to “real time” as possible. There are several levels of audit frequency, depending on the type of audit:
- Frequent: Operational (e.g., inspections, housekeeping, maintenance) – done as part of routine day-to-day operational responsibilities
- Periodic: Compliance, systems, actions/projects – conducted annually/semi-annually
- As needed: For issue follow-up
- Infrequent: Comprehensive, independent – conducted every three to four years
4. Robust Corrective Action Program
As mentioned above, corrective actions are a must. If there is no commitment to correction, there is no reason to audit. A robust root cause analysis is essential. This should be a formal, yet flexible, approach. There should be no band-aids. Mistake-proof corrections and include metrics where possible. In the drum example given above, a more robust corrective action program would look at the root cause: Why was the drum mislabeled? Did the person know to label it? If so, why didn’t they do it?
The correction itself is key to the success of the audit program. Establish the expected timeframe for correction (including addressing preventive action). Establish an escalation process for delayed corrections. Corrective actions should be reviewed regularly by upper management using the existing operations review process. There must also be a process for verification that the correction has been made; the next audit cycle may not be sufficient.
Note also that addressing opportunities for improvement, not just non-compliance findings, may increase the return on investment associated with conducting an audit.
5. Sharing of Findings and Best Practices
Audit results should be communicated to increase awareness and minimize repeat findings. Even if conducted under privilege, best practices and corrections can and should still be shared. Celebrate the positives and creative solutions. Stress the value of the audit program, always providing metrics and cost avoidance examples when possible. Inventory best practices and share/transfer them as part of audit program results. Use best-in-class facilities as models and “problem sites” for improvement planning and training.
Value-Added Audit
An audit can provide much additional value and return on organization if it is planned and managed effectively. This includes doing the following:
- Align program goal with business strategy to secure top-down buy-in
- Expand criteria beyond compliance
- Gain goodwill through positive approach
- Document program and results
- Monitor for timely, effective corrective action
- Share opportunities for improvement

Compliance Risk Assessment
Compliance risk assessment helps to identify and assess risks related to applicable regulatory requirements. Internal and external events or conditions affecting the entity’s ability to achieve objectives must be identified, distinguishing between risks and opportunities. These risks are analyzed, considering the following:
- Size of the risk – where, how big, how often/many?
- Severity of the outcome – to what extent can it impact safety, environmental, operational, financial, customer relations, regulatory compliance?
- Likelihood/probability of each risk – how likely is the occurrence of a negative outcome, considering the maturity of existing controls?
Based on this assessment, management can prioritize risks, select appropriate risk responses (avoiding, accepting, reducing, sharing), and develop a set of actions to align with the entity’s risk tolerance/appetite. An acceptable level of residual risk is considered after selected improvements and controls are applied. From there, policies and procedures can be established and implemented to help ensure the risk responses are effectively communicated so operating managers and individuals can carry out their responsibilities.
A deeper dive compliance program assessment may be performed for those risks that are identified as the company’s most significant.
Compliance Program Assessment
A compliance program assessment looks beyond “point-in-time” compliance to critically evaluate how the company manages compliance programs, processes, and activities, with compliance assurance as the ultimate goal. Capability, capacity, programs, and processes to comply are examined as part of this review. Conducting routine process and compliance audits are also key components of a compliance assurance program.
Compliance program assessment should follow a disciplined and consistent process, resulting in an effective program that guides alignment of activities to an integrated management system for sustained compliance and continuous improvement. An essential part of the assessment, audits capture regulatory compliance status, management system conformance, adequacy of internal controls, potential risks, and best practices.
Compliance program assessment enables a company to define and understand:
- Compliance requirements and where regulated activities occur throughout the organization
- Current company programs and processes used to manage those activities and the associated level of program/process maturity
- Deficiencies in compliance program management and opportunities for improvement
- How to feed review recommendations back into elements of the management system to create a roadmap for sustaining and continually improving compliance
There are six phases associated with a compliance program assessment:
Phase 1 – Regulations, Requirements, and Applicability Analysis: Phase 1 focuses on identifying, organizing, validating, and understanding all of the requirements (legal or other) with which the company must comply. It provides an applicability analysis of the requirements to company operations by functional area and evaluates the associated risks. This stage engages representatives across the company who are responsible for activities subject to the requirements.
Phase 2 – Activities Analysis: This phase involves developing an inventory/profile of all company activities that may trigger the requirements identified in Phase 1. It asks the question, “What activities does the company carry out that are covered by the requirements?”
Phase 3 – Desired Compliance Program Standard: Establishing the company’s expectations for compliance program processes and controls—the desired condition—is essential. This “to-be” standard integrates management system principles into compliance program management. Programs should examine relative risks and ensure that risk-based priorities are being set.
Phase 4 – Actual Compliance Program Condition: In contrast to the desired standard identified in Phase 3, Phase 4 is about describing the company’s current compliance program. It defines how the company performs the activities outlined in Phase 3 (along with who, when, and where)—the “as-is” condition. This is done in the same framework as the desired standard in order to compare them in the next phase.
Phase 5 – Gap Analysis: The gap analysis compares actual compliance program management against the desired standard. It evaluates compliance program management processes, controls, and maturity to determine if they are good as is, need improvement, or are missing. These gaps and opportunities provide the basis for the improvement actions developed in Phase 6.
Phase 6 – Improvement Actions: Phase 6 moves the process along to developing action plans and an approach for ongoing management review that will guide the compliance program development and improvement activities. Compliance program management review is established at the end of this last phase. If there is a management system in place, program review information and action plan tracking can be integrated into that management system.
Outcomes
As a whole, this process will help companies evaluate the degree to which:
- Compliance goals and objectives are set and communicated by management.
- Hazards and risks are identified, sized, and assessed, including an inventory of activities subject to the compliance requirements and the relative risks.
- Existing controls are adequate and effective, recognizing, and addressing changed conditions.
- Plans are in place to address risks not adequately covered by existing controls.
- Plans and controls are resourced and implemented.
- Controls are documented and operationalized across functions and work units.
- Personnel know and understand the controls and expectations, and are engaged in their design and improvement.
- Controls are being monitored with appropriate metrics and compliance auditing and assurance.
- Information system is sufficient to support management system-required functions (e.g., document management and control, action tracking, notifications, training tracking, task calendaring, metrics reporting). Information dashboards can be used for reports to management.
- Deficiencies are being addressed by corrective/preventive action and are being tracked to completion.
- Processes, controls, and performance are being reviewed by management for ongoing improvement, including the maintenance and continual improvement of the integrated management system.

Maintaining a Compliance Assurance Program
A well-designed and well-executed compliance assurance program provides an essential tool for improving and verifying business performance and limiting compliance risks. Ultimately, however, a compliance program’s effectiveness comes down to whether it is merely a “paper program” or whether it is being integrated into the organization and used in practice on a daily basis.
The following can show evidence of a living, breathing program:
- Comprehensiveness of the program
- Dedicated staff and resources
- Employee knowledge and engagement
- Management commitment and employee perception
- Internal operational inspections, “walkabouts” by management
- Independent insider, plus third-party audits
- Program tailoring to greatest risks
- Consistency and timeliness of exception (noncompliance/nonconformance) disclosures
- Tracking of timely and adequate corrective/preventive action completion
- Progress and performance monitoring
Best Practices
To achieve a compliance assurance program on par with world-class organizations, there are a number of best practices that companies should employ:
Know the requirements. This means maintaining an inventory of regulatory compliance requirements for each compliance program, as well as of state/local/contractual binding agreements applying to operations. It is vital that the organization keep abreast of current/upcoming requirements (federal, state, local).
Plan and develop the processes to comply. Identify and assess compliance risks, and then set objectives and targets for performance improvement based on top priorities. From here, it becomes possible to then define program improvement initiatives, assign and document responsibilities for compliance (who must do what and when), develop procedures and tools, and then allocate resources to get it done.
Assure compliance in operations. The organization needs to establish routine checks and inspections within departments to evaluate conformance with sub-process procedures. Process audits should be designed and implemented to cut across operations and sub-processes in order to evaluate conformance with company policies and procedures. Regulatory compliance audits should further be conducted to address program requirements (e.g., environmental, safety, mine safety, security). Audit performance must be measured and reported, and the expectations set for operating managers to take responsibility for compliance.
Take action on issues and problems. Capture, log and categorize noncompliance issues, process nonconformances, and near misses. Implement a corrective/preventive action process based on the importance of issues. Be disciplined in timely completion, close-out, and documentation of all corrective/preventive actions.
Employ management of change (MOC) process. Robust MOC processes help ensure that changes affecting compliance (to the facility, operations, personnel, infrastructure, materials, etc.) are reviewed for their impacts on compliance. Compliance should be assured before the changes are made. Failure to do so is one of the most common root causes of noncompliance.
Ensure management involvement and leadership. Set the tone at the top. The Board of Directors and senior executives must set policy, culture, values, expectations, and goals. It is just as important that these individuals are the ones to communicate across the organization, to demonstrate their commitment and leadership, to define an appropriate incentive/disincentive system, and to provide ongoing organizational feedback.
Maintaining Ongoing Compliance
The compliance assurance program must be a living, breathing program. As risks change, the program must be refreshed, refined, and redeployed. A management system framework can help ensure operational sustainability. A management system drives the auditing process and helps companies say what they will do, do what they say and, importantly, verify it.
Together, there is a real value at the intersection of a compliance assurance program and management systems. Management systems define the internal controls that are in place to reduce risks, prevent losses, and sustain and improve performance over time through the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle of continual improvement.
Testing and Monitoring
Testing, monitoring, and measuring are crucial elements of this cycle. Without them, it is difficult to understand what is working and what needs improvement. Robust testing and monitoring programs can serve as early warning systems for identifying potential compliance risks before they become enforcement issues.
Compliance should be tested and monitored throughout each level of the organization. A strong testing program will evaluate the results of the compliance risk assessment and assign compliance risks to the business units and processes where they are most likely to occur, creating clear lines of responsibility and accountability. Key risks and the related controls should be tested periodically using statistically valid sampling methodologies, and monitoring activities should be performed on an ongoing basis. Doing so produces trend data that provides the rationale needed for making changes to underlying business processes, as well as emerging risks.
Ongoing compliance excellence relies on top management, operations managers, EHS personnel, and individual employees throughout the organization working together to build and sustain an organizational culture that places compliance on par with business performance. Senior management must focus on the overall culture of the company in terms of taking the necessary steps to reduce risk and make prevention part of daily operations. While it may be impossible to eliminate all risk exposure, a solid risk framework, assessment methodology, and compliance assurance program can help to prioritize risks for active management, sustained compliance, and positive business impacts.

Environment / Food Safety / Quality / Safety / Technology Enabled Business Solutions
Comments: No Comments
Technology & the 8 Functions of Compliance
Virtually every regulatory program—environmental, health & safety, security, food safety—has compliance requirements that call for companies to fulfill a number of common compliance activities. While they do not necessarily need to be addressed all at once or from the start, considering the eight functions of compliance (as outlined below) when designing a compliance Information Management System (IMS) helps define the starting point and build a vision for the “end point” when planning IMS improvements. These compliance functions translate into modules—facility profiles, employee counts, training tracking, corrective action tracking, auditing tasks, compliance calendars, documents and records management, permit tracking, etc.—that are instrumental in establishing or improving a company’s capability to comply.
8 Functions of Compliance
- Inventory means taking stock of what exists. The outcome of a compliance inventory is an operational and EHS profile of the company’s operations and sites. In essence, the inventory is the top filter that determines the applicability of regulatory requirements and guides compliance plans, programs, and activities. For compliance purposes, the inventory is quite extensive, including (but not limited to) the following:
- Activities and operations (i.e., what is done – raw material handling, storage, production processes, fueling, transportation, maintenance, facilities and equipment, etc.)
- Functional/operational roles and responsibilities (i.e., who does what, where, when)
- Emissions
- Wastes
- Hazardous materials
- Discharges (operational and stormwater-related)
- Safety practices
- Food safety practices
- Authorizations, permits & certifications provide a “license to construct, install, or operate.” Most companies are subject to authorizations/permits at the federal, state, and local levels. Common examples include air permits, operating permits, Title V permits, safe work permits, tank certifications, discharge permits, construction authorization. In addition, there may be required fire and building codes and operator certifications. Once the required authorizations, permits, and/or certifications are in place, some regulatory requirements lead companies to the preparation and updating of plans as associated steps.
- Plans are required by a number of regulations. These plans typically outline compliance tasks, responsibilities, reporting requirements, schedule, and best management practices to comply with the related permits. Common compliance-related plans may include SPCC, SWPPP, SWMP, contingency, food safety management, and security plans.
- Training supports the permits and plans that are in place. It is crucial to train employees to follow the requirements so they can effectively execute their responsibilities and protect themselves, company assets and communities. Training should cover operations, safety, security, environment, and food safety aimed at compliance with regulatory requirements and company standards and procedures.
- Practices in place involve doing what is required to follow the terms of the permits, related plans and regulations. These are the day-to-day actions (regulatory, best management practices, planned procedures, SOPs, and work instructions) that are essential for following the required processes.
- Monitoring & inspections provide compliance checks to ensure locations and operations are functioning within the required limits/parameters and the company is achieving operational effectiveness and performance expectations. This step may include some physical monitoring, sampling, and testing (e.g., emissions, wastewater). There are also certain regulatory compliance requirements for the frequency and types of inspections that must be conducted (e.g., forklift, tanks, secondary containment, outfalls). Beyond regulatory requirements, many companies have internal monitoring/inspection requirements for things like housekeeping, sanitation, and process efficiency.
- Records provide documentation of what has been done related to compliance—current inventories, plans, training, inspections, and monitoring required for a given compliance program. Each program typically has recordkeeping, records maintenance, and retention requirements specified by type. Having a good records management system is essential for maintaining the vast number of documents required by regulations, particularly since some, like OSHA, have retention cycles for as long as 30 years.
- Reports are a product of the above compliance functions. Reports from ongoing implementation of compliance activities often are required to be filed with regulatory agencies on a regular basis (e.g., monthly, quarterly, semi-annually, annually), depending on the regulation. Reports also may be required when there is an incident, emergency, recall, or spill.
Reliable Compliance Performance
Documenting procedures on how to execute these eight functions, along with management oversight and continual review and improvement, are what eventually get integrated into an overarching management system (e.g., environmental, health & safety, food safety, security, quality). The compliance IMS helps create process standardization and, subsequently, consistent and reliable compliance performance.
In addition, completing and organizing/documenting these eight functions of compliance provides the following benefits:
- Helps improve the company’s capability to comply on an ongoing basis
- Establishes compliance practices for when an incident occurs
- Creates a strong foundation for internal and 3rd-party compliance audits and for answering outside auditors’ questions (agencies, customers, certifying bodies)
- Helps companies know where to look for continuous improvement
- Reduces surprises and unnecessary spending on reactive compliance-related activities
- Informs management’s need to know
- Enhances confidence of others (e.g. regulators, shareholders/investors, insurers, customers), providing evidence of commitment, capability, reliability and consistency in the company’s compliance program
