
EHS Experts Roundtable
We recently sat down with three of KTL’s environmental, health, and safety (EHS) experts, Becky Wehrman-Andersen, Liz Hillgren, and Jake Taylor, to talk about all things EHS. The three Senior Consultants shared what they are seeing in the marketplace, as well as some of their best advice and lessons learned for managing EHS compliance.
What are some of the biggest EHS issues you see your clients facing right now?
Collectively, there are a few trends we see time and again, which generally can be tied back to many EHS “departments” (which often consist of just one person) lacking the resources—financial and personnel—to manage the sheer number of EHS requirements they are required to comply with.
We find that EHS personnel are being asked to manage a lot—and often in areas that may be outside their education/expertise/experience. So while they may have knowledge, in part, of EHS regulations, they often don’t have a comprehensive enough knowledge to always even know what they are missing. Add to this the fact that there is almost “too much” information available, and it can very quickly become overwhelming to determine what is applicable and what needs to be done to comply.
We see this creating several common scenarios:
- Entire compliance programs are being missed because customers do not realize they are subject to some requirements. In some cases, companies just don’t know what they don’t know.
- Frequently, companies may not understand the thought process of what needs to be in place to satisfy a standard’s requirements. For example, they may have OSHA training programs in place to meet requirements; however, they do not have the accompanying site-specific written programs and/or documentation that are also required for compliance.
- Often customers do not take the time or have the knowledge to identify the riskiest chemicals or processes onsite, which leads to elevated challenges in keeping employees and the surrounding environment safe.
How have you seen COVID impacting industry/your clients?
The majority of our clients have really adapted and responded to COVID as best they can. Many have remained busy and are doing just fine. However, the pandemic has resulted in operational challenges—from expanding shifts to separate people more, to having more “virtual workers,” to managing internal safety cost increases, to developing plans to juggle outbreaks. In some cases, this has slowed some policy/program development and impacted company culture. In addition, we are seeing a few companies experiencing supply chain challenges but to a lesser extent than anticipated. Understandably, there is also an element of frustration as guidance remains in flux, as well as concern as facilities “button up” for winter due to the elevated risks associated with closed spaces with little air circulation.
At the same time, companies are learning how to work with fewer people and conduct some business activities virtually. And many have been pushed into using technology that may have been available in the past but was never a necessity of doing business. Even though there have been some “bumps” in the road, people are catching on. In fact, KTL has been conducting audits, assessments, and training virtually, and our clients are seeing the benefits of a virtual approach on many levels. We anticipate some of this will continue as the new norm due to the business efficiencies it presents.
Are there any recent regulatory developments (or any on the horizon) that industry should be preparing for?
EPA has a provision as part of the 2016 Hazardous Waste Generator Improvements Rule that will be affecting small quantity generators (SQG) in 2021. The Agency is now requiring SQGs to renotify EPA or their state agency about their hazardous waste activities every four years. The first renotification is due by September 2021. Since this is the first time EPA is requiring this of SQGs, many are not as aware of the Hazardous Waste Generator Improvements regulations and this specific renotification requirement. It is one that will impact many. Read more from EPA.
Other regulatory changes on the forefront will likely depend largely on the outcomes of the election this November, and it is just too soon to predict.
Based on your experience, what are some best practices you would recommend to help companies ensure ongoing EHS compliance and meet business objectives?
- Conduct a comprehensive gap assessment to ensure you are meeting the requirements of all applicable EHS regulations. This should be the starting place for understanding your regulatory obligations and current compliance status.
- Organize your records. Know what records you need. Document your inspections and your training. Develop standard operating procedures (SOPs) so people know what to do.
- Seek third-party oversight. Having external experts periodically look inside your company provides an objective view of what is really going on, helps you to prepare for audits, and allows you to implement corrective/preventive actions that ensure compliance.
- Perform a comprehensive onsite risk assessment with associated risk minimization planning and plan/conduct annual spill drills to practice emergency response for hazardous chemical incidents.
- Create an integrated management system (e.g., ISO 9001/14001/45001, Responsible Distribution) by finding commonalities between the standards and leveraging pieces of each to develop a reliable system that works for your organization.
- Develop a relationship with someone you trust to do things in your best interest, understanding that EHS should be a process of continuous improvement. Use them to help you understand what regulations apply. Let them help you prioritize your compliance plan. Use them to do your annual training. Rely on them as a part of your team.
- Get senior leadership commitment. It is often clear how an organization prioritizes EHS with little digging. Even with the best EHS personnel, the organization and its EHS system will only be as good as the top leadership and what is important to them.
Do you have any good “lessons learned” to share about what to do when it comes to EHS compliance?
Just start! It is better to do some than none. Get organized. Determine what you need, break it down, set a schedule, use your consultant to keep you on target, and just get started. Something is definitely better than nothing.
KTL has coached several companies from a “zero to compliance” status and has also actively assisted in OSHA and EPA penalty negotiations. One company went from an anticipated $300,000 – $500,000 in penalty to ZERO penalty, reduced their generator status from large quantity generator (LQG) to very small quantity generator (VSQG), and achieved a more than 70% reduction in waste management costs simply through process changes and risk reduction strategies.
How important is technology when it comes to EHS compliance?
EHS personnel are starting to see the possibilities of how incorporating technology solutions can help them become more efficient in their operations and compliance processes. As stated above, COVID has pushed some technology innovations to the forefront as a means for companies to continue operating in different ways.
For example, technology tools can be very helpful with tracking requirements and documents—but it also requires good organization and communication. Custom apps for conducting inspections and regular checklists can be a simple way to create operational efficiencies, particularly for smaller organizations who may lack the initial financial resources to undertake an entire system implementation. Once that initial investment is made, companies often see the value of technology and the potential to implement a centralized compliance information management system to help manage and track compliance obligations, activities, and performance/status.
With technology, it is no longer a question of IF, it is just a matter of WHEN companies decide to jump on board. Technology and “Big Data” can—and should—be a focus of any EHS compliance program. The investment will pay off in the end.
What value do you see KTL providing?
We serve as an extension of a company’s EHS staff—from completing small tasks that never seem to get done to identifying large gaps in compliance and building systems to resolve those non-compliance issues. We are there to support, answer questions, provide technical knowledge, and help our customers achieve compliance. We are teachers, trainers, a sounding board, and an EHS support system. We have a great team of experts who know EHS, understand industry, and excel at creating solutions and tools to meet our clients’ needs. Trust is critical and we strive to be trustworthy. That is who KTL is.

Environment / Food Safety / Quality / Safety / Technology Enabled Business Solutions
Comments: No Comments
Functionality for Today…Flexibility for the Future
There is no question about it—organizations across nearly every industry are relying more heavily on information technology (IT) to carry out daily tasks, connect staff, and manage operations. Technology can also play a vital role in managing compliance requirements.
For example, we recently shared a case study demonstrating how leveraging a simple Microsoft SharePoint®-based Compliance Management System (CMS) has provided Southeast Missouri State University (SEMO) with access to the data, documents, systems, and processes required to help employees effectively manage compliance requirements—even when working remotely.
Tips to Design a Successful CMS
A CMS is used to coordinate, organize, control, analyze, and visualize information to help organizations remain in compliance and operate efficiently. When building a CMS, it is important to follow a process to design a system that provides the functionality to meet current requirements and the flexibility to anticipate future needs.
The following eight tips can help ensure you end up with the right CMS and efficiency tools to support your organization for the long term:
- Inventory your existing systems – Identify how you are currently managing your compliance needs/requirements. What’s working well? What isn’t working? Do the systems work together? Do they all operate independently? This inventory should evaluate the following:
- Current systems and tools
- Status and functionality of existing processes
- Data sources and ability to pull information from various sources
- Organizational complexity
- Compliance status
- Existing management systems
- Determine your business drivers – Are you looking to save time? Create efficiencies? Provide access to enable employees to work from home? Reduce the number of resources required? Have better access to real-time information? Answer to senior management? Respond to regulatory requirements? These drivers will also drive the decisions you make when it comes to module development, dashboard design, reporting, and more.
- Understand the daily routine of the individuals using the system – Systems and modules should be built according to existing daily routines, when possible, and then implemented and rolled out in a way that encourages adoption. Having a solid understanding of routine tasks and activities will ensure the system is built in a way that works for the individuals using it—and for the way they will be accessing it.
- Understand your compliance requirements – Do you have permitting requirements? Does your staff need training? How do you maintain your records? Are there regular (e.g., annual, semi-annual) plans and/or reports you need to submit? Do you have routine inspections and monitoring? All these things can and should be built into a CMS so they can be managed more efficiently.
- Get the right parties involved – There are many people that touch a CMS at various points in the process. The system must be designed with all these users in mind: the end user entering data in the field, management who is reading reports and metrics, system administrator, office staff, etc. A truly user-friendly system will be something that meets the needs of all parties. If employees are frustrated by lack of understanding, if the system isn’t intuitive enough, if it is hard to put data in or get metrics out, the system will hold little value.
- Make your wish list – While you may start your project one module at a time, it is important to define your ultimate desired end state. In a perfect world, how would the CMS operate? What parts and components would it have? How would things work together? What type of interfaces would users have? You may build piece by piece, but you must develop with the end in mind.
- Set your priorities, budget, and pace – What is the most important item on your list? Do you want to develop modules one at a time or as a fully functional system? It often makes sense to start where you already have processes in place that can be more easily transitioned into a new system to encourage user buy-in. Priorities should be set based on ease of implementation, compliance risk, business improvement, and value to your company.
- Select the right consultant – For a CMS, it is valuable to have a consultant who doesn’t just understand technology but also understands your operational needs, regulatory obligations, and compliance issues. More than likely, off-the-shelf software will not be a silver bullet compliance solution. A consultant who can understand the bigger picture of where you want to go and will collaborate to design the right CMS and efficiency tools will bring the most value to your organization.
These tips can help ensure any organization designs and develops the right CMS—one that works within the organization’s operating environment—to reduce compliance risk, create efficiencies, provide operational flexibility, and generate business improvement and value.

Taking Training Virtual…Or Not
Over the past several months, many companies have had to prioritize business activities given restrictions on travel and social distancing guidelines. Despite these restrictions, however, certain compliance activities are still required, including training.
Training is a key component for maintaining ongoing compliance—whether with regulatory requirements, supply chain mandates, or internal policies. While some training can be postponed, putting training on the backburner can have its consequences, ranging from unprepared employees, to noncompliance, to preventable injuries or worse.
Much like with audits, there are alternatives to meeting training requirements and ensuring employees are well-instructed and prepared to do their jobs, even with current government and/or company restrictions. Online and virtual training are not necessarily new options, but their popularity is most certainly on the rise. In-person, online, and virtual training can all provide quality options if you understand your training needs and understand what type of training works best in different scenarios.
Face-to-Face
As we have experienced, sometimes there is no substitute for doing things face-to-face. For certain types of training, in-person is clearly the best alternative for a number of reasons:
- It is designed for people who need to genuinely know the material inside and out and for those who would benefit from a more tailored, interactive learning experience.
- With in-person training, learners are able to ask specific questions and get them answered immediately.
- In-person training provides a focused, immersive learning experience, where attendees can have interaction, discussion, and live input.
- Trainers get to know attendees and can adjust training (e.g., material, learning speed, examples) to the group’s learning style.
- In-person training allows attendees to develop relationships with the trainer and other attendees, which can prove beneficial on future projects.
As many organizations have discovered, particularly lately, while in-person training may offer a great alternative, it is not always possible. Beyond travel and social distancing restrictions, in-person training can also be cost-prohibitive. In addition, scheduling of in-person training can present more challenges, as timing is based on the instructor and is not flexible.
Best suited for: Multi-day classes where demonstration of competency is needed, and participants are building skills they will use frequently; introductory classes where participants need to understand new material.
The Online Option
At the other end of the spectrum, we have online training (not to be confused with virtual, which is discussed below). Online training involves an online module that allows participants to watch and/or listen to a pre-recorded class. Generally speaking, online training works best when individuals already know the material (e.g., refresher training) and is most appropriate when the attendee does not have to be an expert in the subject matter (i.e., awareness level vs. functional expertise).
In addition, online training is generally cheaper since it is not customized and does not require travel or an onsite trainer. It can also be faster and more flexible, as attendees can work at their own pace and have the ability to pick their own schedule.
While there are certain benefits to online training, it is not suitable for all types of training. Because online training does not involve a live instructor, attendees are generally unable to ask questions effectively and there is little opportunity for follow-up input on areas covered. This is no opportunity for hands-on learning and interaction. For example, something like 24-hour HAZWOPER training would be difficult to do as an online course, as a hands-on component is valuable in helping participants demonstrate competency, as required. Finally, because of a potentially diverse audience, online training tends to be generic and not tailored to the specific needs.
Best suited for: Courses where participants have had many, many years of experience and just need refreshers, such as HAZWOPER 8-hour, DOT General Awareness, or RCRA refresher training.
Taking It Virtual
Finally, virtual training provides a bridge between online and in-person training. Like online training, virtual training is done via technology (e.g., Zoom, WebEx); however, it takes place live with instructors engaged in the training as it is occurring. Virtual has many of the same advantages as in-person training since it is being done live. Learners can get more in-depth training and benefit from live interaction, questions, and discussion to help develop specialized expertise. Virtual training works best when travel is limited but students still need to have real-time input from the instructor.
That being said, virtual training cannot completely replace in-person training. With screens, it may be difficult for the trainer to read the crowd and accurately interpret learning needs. Hands-on opportunities become more limited—though not impossible—and require cooperation, coordination, and open-mindedness from all attendees. Finally, technology and logistics are critical for this type of training. A computer with good internet access is critical. If internet connections are slow or sound quality is poor, training can quickly become ineffective.
Best suited for: Refresher training (as with online options), more detailed training that can be customized to the specifics of the class (i.e., site-specific, industry-specific), or training for those with less experience who may need to ask questions.
Consider Learning Styles
People learn very differently. Some people are aural learners and can hear material and develop understanding. Others are visual learners so just reading material on a screen “sticks.” Others are tactile learners and need to participate in physical interaction to understand content. It is important to keep this in mind when choosing the best platform, as well:
- With in-person classes, all learner types can be addressed.
- With online classes, typically only visual learners retain the information unless there is audible training coordinated with the material.
- With virtual learning and coordination with the site prior to the training program, all three learner types can be addressed.
While some training can be rescheduled with minimal impacts to the business, many training requirements cannot. Companies need to know their workers are retaining the information, particularly given OSHA requirements that employees must demonstrate understanding and competency. To ensure that training not only “checks the box” but is also effective, it is important to evaluate not just the training, but the delivery options. In-person, online, and virtual all have their strengths based on the training needs and individual learning styles.

Environment / Kestrel Tellevate News / Safety / Technology Enabled Business Solutions
Comments: No Comments
KTL Renews Agreement to Provide Access to EHS Regulatory Question Modules
KTL is pleased to announce that we have renewed our agreement with the Construction Engineering Research Laboratory (CERL) of the U.S. Army Corp of Engineers, which provides access to the following regulatory question modules:
- The Environmental Assessment and Management (TEAM) Guide and the related state supplements address environmental compliance in the areas of air quality, cultural and natural resources, hazardous materials and waste, pesticide management, pollution prevention, energy conservation, petroleum, oils and lubricants, storage tanks, solid waste management, toxic substances, water quality, and more.
- The Occupational Safety and Health (OSH) Guide is used in assessing compliance with the standards of the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). It may also be used in combination with an agency-specific safety and occupational health manual. The OSH Guide is based on OSHA regulations from Title 29 of the Code of Federal Regulations.
KTL originally entered into this agreement with CERL in 2015. CERL’s experts are dedicated to conducting ongoing research, updating federal and state environmental and federal safety regulatory requirements, and developing and maintaining standardized audit checklists for those regulations. These checklists are very comprehensive; are used by auditors for DOD, DOE, DOI, and other federal agencies; are updated regularly to reflect any regulatory changes; and cover virtually all of the functions that would be present in a broad mix of industrial companies.
Our agreement allows KTL to make the TEAM Guide and OSH Guide available through an electronic format (i.e. dynaQ™). KTL staff can use these modules to stay current on changing federal regulations. The question modules bring a basis of significant credibility related to the reliability and completeness of audit content via a software tool that manages audit data and makes finding information more efficient. With this agreement, KTL remains one of the only professional service firms in the country to offer access to the following regulatory question modules.

Comments: No Comments
COVID-19 & Emerging Best Practices for Waste Management
The COVID-19 pandemic has had tremendous impacts on various industries and sectors—most have had to adjust business practices (in small or large ways) to meet new guidelines for safe operations. At times, it may seem impossible to keep up with the latest developments/recommendations and their impacts on day-to-day operations.
A cross-cutting issue for almost every business (and every household) is the safe and proper management of waste. Almost all our activities generate some form of waste. During an infectious disease outbreak such as COVID-19, it becomes increasingly important to ensure the provision of safe water, sanitation, and hygienic conditions to help prevent human-to-human transmission of the virus.
Updated Guidance
State and federal agencies throughout the U.S. and abroad, as well as international organizations, have begun to issue new and/or update existing guidance regarding proper waste management practices as experts learn more about the COVID-19 virus (SARS-CoV-2). The U.S. Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), for example, recently issued guidance stating that, “Generally, management of waste that is suspected or known to contain or be contaminated with COVID-19 does not require special precautions beyond those already used to protect workers from the hazards they encounter during their routine job tasks in solid waste and wastewater management.” However, state, tribal, and local governments may follow stricter guidance.
Similarly, the World Health Organization (WHO), in its April 2020 revised Interim Guidance, noted that there is “no evidence that direct, unprotected human contact during the handling of healthcare waste has resulted in the transmission of the COVID-19 virus.” The WHO further states that the usual best practices for the safe management of infectious waste should be exercised.
Best Practices to Minimize Risk
The OSHA and WHO guidance highlight an important point—where existing processes and systems can safely be relied upon for the proper management of waste during this pandemic, organizations should avoid making changes. Where the nature of COVID-19 requires adjustments, that is where organizations should focus their efforts.
Outlined below are some general best practices that organizations should consider implementing to minimize risks associated with waste management during COVID-19 and beyond:
- Municipal Waste: Workers and employers should manage municipal (e.g., household, business) solid waste with potential or known COVID-19 contamination like any other non-contaminated municipal waste. Workers should prevent exposure to waste through safe work practices and approved Personal Protective Equipment (PPE), such as puncture-resistant gloves and face and eye protection. To help protect sanitation workers, the Idaho Department of Environmental Quality (DEQ) advises households with waste suspected to be infected with COVID-19 tightly enclose waste in heavy-duty bags, double-bag the waste, and ensure that curbside containers can close completely. As always, anyone handling waste should wash hands thoroughly.
- Healthcare Waste: Healthcare waste with potential or known COVID-19 contamination should be managed like any other regulated medical waste. In the U.S., COVID-19 is not a Category A infectious substance. Again, use typical engineering and administrative controls, safe work practices, and PPE to prevent worker exposure. Although not required, the Healthcare Waste Institute (HWI) recommends COVID-19 waste be identified to protect workers in the event a bag needs to be re-opened. Only grossly contaminated PPE should be placed into sealed bags (red bags in the U.S.). Tissues or similar materials used by patients when coughing or sneezing should be immediately disposed of in a lined waste receptacle, and then correct hand hygiene should be performed. Such waste may be disposed as regular trash (i.e., municipal solid waste), unless otherwise directed by local health departments. Public Health England, for example, advises that such waste be double-bagged, tied securely, stored separately from other waste, and left for 72 hours before sending for disposal as standard municipal solid waste.
- Recycling: As with municipal waste, employers and workers in the recycling industry should continue to use typical engineering and administrative controls, safe work practices, and PPE to prevent exposure to recyclable materials they manage, including any contaminants in the materials. Organizations and households should always refer to their local recycling hauler’s guidelines to determine if and what products can be recycled. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is advising individuals to treat recyclables as trash if anyone in their home has COVID-19.
- Wastewater: Coronaviruses are susceptible to the same disinfection conditions as other viruses, so current disinfection processes in wastewater treatment facilities are expected to be sufficient, per OSHA and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). This includes practices such as oxidation with hypochlorite (i.e., chlorine bleach) and peracetic acid, as well as inactivation using ultraviolet irradiation. There is no evidence to suggest that additional, COVID-19-specific protections are needed for employees involved in wastewater treatment operations.
- General Hygiene and PPE: As currently recommended by all agencies, improved personal hygiene, particularly adequate handwashing and the use of adequate PPE (e.g., masks, gloves, eye protection), offers the greatest protection against COVID-19, including transmission through waste. Staff handling waste should be properly trained, use approved PPE, and maintain good hygiene.
As with many facets of this pandemic, regulatory requirements and best practices are subject to change as we continue to learn about the virus and its transmission. KTL can help you monitor these developments and understand which requirements and guidance apply to your operations—both in the U.S. and abroad.

Virtual Audits: Best Practices to Make Them Work
Audits provide an essential tool for improving and verifying compliance performance. Audits may be used to capture regulatory compliance status, management system conformance, adequacy of internal controls, potential risks, and best practices.
Most regulations, standards, and guidance require audits to be conducted with some established frequency. For many companies, figuring out how to meet these audit requirements amongst travel restrictions, new company safety protocol, and government quarantines related to COVID-19 presents a significant new challenge.
The Online Alternative
Companies come in a variety of sizes with a range of different needs. Because of this, auditing standards remain fairly flexible by design. Fortunately, this allows for online/remote/virtual audits as a viable alternative to onsite audits—provided the audits:
- Are planned well;
- Appropriately leverage technology; and
- Are executed by a team who understands the facility and the requirements.
The ultimate objective of a virtual audit remains the same as an in-person audit: To obtain credible audit evidence to accurately assess compliance/conformance with identified requirements/specifications. The difference lies in the means in which that evidence is collected (i.e., live stream video, surveillance cameras, group web meetings, electronic document review).
Weighing Risks vs. Rewards
Audits can be conducted onsite, remotely, or a combination of the two. In many cases, companies may already be having portions of the audit (e.g., document review) done remotely. Moving the entire audit to the virtual world allows credible evidence to be obtained in unique ways that can offer significant benefits to a company when onsite audits aren’t possible—and even when they are:
- Reduced cost – Online audits eliminate the expenses associated with travel (i.e., mileage, flights, hotels, meals), which can add up depending on the location and duration of the audit.
- Flexible schedule – Remote audits can be conducted on a more flexible time schedule. Auditors do not have to complete work onsite in a set number of days, as is required when traveling to a facility. The auditor can also review areas in question remotely after the audit is technically over. Note that a more flexible time schedule does not necessarily mean less time involved to conduct the audit.
- Social distancing – As CDC guidelines have recommended, it is currently safest to work remotely, when possible, or to remain six feet of social distance to avoid potential transmission of COVID-19. Through the use of technology, virtual audits provide a social distancing extreme.
- Improved systems – Preparing for a virtual audit provides the “push” some organizations need to improve electronic storage systems. To conduct a virtual audit, documents and records must be retained in an organized manner that facilitates easy/quick access. Being able to access all documents remotely is necessary—paper records or documents stored on individual computers/network drives no longer cut it.
At the same time, there are some potential risks to conducting a completely virtual audit, particularly since this practice is relatively new to many organizations:
- Observation/technology limits – Observation of site conditions is limited by the ability to direct live stream video remotely. Technology can create limitations. If the camera can’t see it, neither can the auditor. Poor video quality can impede visual clarity. You don’t know what you don’t know.
- Communication confusion – It can be difficult to read body language and/or interpret emails and phone conversations to make sure communication is clear. This can require revisiting topics/findings several times to ensure accurate evidence is collected.
- Time barriers – There may be time zone and associated scheduling barriers depending on the location of the auditor and the facility.
Considerations and Best Practices
Regardless of the type of audit a facility conducts (i.e., remote, onsite, combination), standard audit best practices should be followed to ensure that audit results are comprehensive and credible. If the company opts for a virtual audit—for any reason—there are a number of considerations and best practices to ensure that the audit effectively fulfills its objectives and alleviates the risks outlined above to the extent possible:
- Site Familiarity – Virtual audits work best if auditors are familiar with the industry and/or operations. While it is not necessary for the auditor to have visited the site before, that type of familiarity with the facility provides the best-case scenario, especially for compliance audits, as it prepares the auditor to know what to look for (and where) and what questions to ask.
- Careful Planning – Much like onsite audits, virtual audits require careful upfront planning on the part of the auditor and the facility—and perhaps to an elevated degree.
- The facility needs to collect all documents and records prior to the audit and determine best way to present that information remotely (e.g., email/transfer ahead of time, allow access to company Intranet/shared directory space, share during a web meeting).
- Interviews are best scheduled in advance to ensure availability; however, they can be conducted on an ad hoc basis as need arises.
- It is best to plot out route and areas of specific focus for the audit ahead of time using a site map as a guide to ensure that all areas are covered and that the audit can be conducted as efficiently as possible using the allocated facility resources. An audit site guide must be assigned who is familiar with the entire facility.
- Technology needs and requirements must be evaluated, and logistics and access should be tested prior to the audit. It is vital that all cameras, web meetings, shared document space, WiFi, and other technology is working appropriately prior to the audit or a lot of time can be wasted troubleshooting issues.
- Video – Videos should be live. Site walks should be led by a site guide/employee along the planned route with smart phones, iPads, etc., with live streaming capabilities. It is important to ensure that live streaming works within the facility being audited so auditors have a clear view of site conditions. Auditors can also take advantage of any in-house surveillance cameras (e.g., security or quality systems) to provide additional footage of operations, when necessary. In most cases, surveillance footage cannot replace live video.
- Web Meetings – Opening, closing, and daily briefings can be conducted via web meeting. Remote audits provide the flexibility to conduct the audit in segments, with briefings following each segment. This allows the auditor to review video footage, evaluate records, and generate questions to ensure the information collected is accurate and complete.
Companies all over the world are working through a transition period right now, where they are trying to establish what a new “normal” looks like when it comes to operating practices, employee health and safety, business continuity, and compliance. Audits are one piece of the overall puzzle that can be transitioned somewhat seamlessly with the right planning and technology in place to ensure ongoing compliance.

Managing Projects & Permits
How many permits does your operating system (e.g., facilities, production, storage, transportation, distribution) have? What kinds of requirements are associated with each of those permits? Who is responsible for making sure requirements are fulfilled? Are there key/critical dates? How many contractors/vendors do you have carrying out activities pertaining to the many diverse permit requirements? How do you manage all that information? And, importantly, how do you verify compliance?
Depending on the breadth and locations of your operations, managing permits and their associated requirements and due dates without a centralized system in place can be an insurmountable challenge. This was certainly true for a large transportation company managing over 3,600 permits for over 1,600 projects across more than 20 states. Finding a better way to track and manage permits wasn’t just a matter of convenience, it was a necessity.
Web-based Tracking System
After a series of washout incidents, the company’s Engineering Department stepped up its efforts to develop a program to ensure engineering and maintenance activities were meeting applicable construction and environmental permit requirements. With so many activities, responsible parties, and deadlines, the Department retained Kestrel Tellevate LLC (KTL) to develop a web-based project tracking system to help:
- Track permit requirements and construction restriction timeframes
- Produce project-specific All Permits Issued (API) documents
- Track post-activity mitigation requirements
- Manage change information
- Report actual-to-budget performance
While the Engineering Department remains responsible for the permitting activities associated with all construction, maintenance, and emergency response activities, KTL’s Permit Tracking System (PTS) offers a cloud-based project management solution to facilitate permit tracking across a variety of data points.
How It Works
The PTS serves as a communication conduit by providing a standardized approach to project/permit activity tracking, while distributing periodic, tailored reports that allow the Engineering Department to manage project activities, as needed. Integrating with internal databases, PTS provides a means to supplement project data with ongoing contractor/consultant input. This enables comprehensive program oversight on the timeliness of the permitting effort and project details, which, in turn, offers preemptive visibility on issues that may affect project construction and permit compliance.
In short, PTS allows the company to:
- Catalog and track permits in one database
- Document and track project conditions, impacts, construction timeframe restrictions, sensitive resources, etc.
- Send and receive notifications of permits about to expire
- Coordinate and communicate with project contractors
- Establish accountability and a standardized approach for reporting and performance measurement
- Effectively manage project process from permitting through handover to construction
- Monitor financial performance
Business Benefits
The Engineering Department has managed nearly 1,600 projects with more than 3,600 associated permits through PTS. Permits in the system include 404 (most common), 401, Floodplain, NESHAPS, FAA, 402, Air, Coast, Air Emissions, 408 Levee, Coast Guard Bridge, Heritage Tree, Tank, Well, Excavated Materials, NPDES, and others.
With this many projects and permits being managed through a consolidated system, PTS is providing many business benefits, including the following:
- Improved program efficiency, consistency, and coherence by fostering a standardized approach to all permitting data management and input by third-party users
- Customized, automated reporting that allows for enhanced progress monitoring, project accountability, and detailed oversight
- Flexible, cloud-based approach to accommodate a variety of program management aspects into a single tool for real-time, comprehensive visibility
- Sole repository for all project management data to help foster communication and coordination both internally and with contractors/consultants
- Improved permit compliance assurance reliability

Getting to the Root Cause
At the most basic level, a root cause is the fundamental reason—or the highest-level cause—for the occurrence of a problem, incident, or event. The root cause sets in motion the entire cause-and-effect reaction that ultimately leads to the problem. Getting to the root cause of any problem is important not just for resolving the issue at hand, but for identifying underlying issues to ensure that similar problems do not occur in the future. This starts with a process called the root cause analysis (RCA).
What Is the Root Cause Analysis (RCA)?
A root cause can be permanently eliminated through process improvement. RCA is a method of problem-solving used to identify the underlying (i.e., root) cause(s) of a problem/incident. RCA can be used to solve problems and provide preventive actions for:
- Major accidents
- Everyday incidents
- Minor near misses
- Human errors
- Maintenance problems
- Medical mistakes
- Productivity issues
- Manufacturing mistakes
- Environmental releases
- Risk analysis, risk mapping
RCA is a systematic process based on the basic idea that effective management requires more than merely putting out fires. RCA focuses on finding a way to prevent these fires from recurring. Rather than just treating symptoms, RCA seeks to identify and address the true, underlying concerns that contribute to a problem or event.
Why is this important? If you just treat the symptoms of the problem, that alleviates them for the short term, but it does nothing to prevent the problem from coming back again. Lasting solutions address the underlying factors—the root cause(s)— that create the problem in the first place. Targeting corrective measures at the identified root causes, subsequently, is the best way to alleviate risk and ensure that similar problems do not occur in the future.
Best Practice
Both the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) encourage organizations to conduct RCA following an incident or near miss at a facility. In fact, facilities covered by OSHA’s Process Safety Management (PSM) standard are required to investigate incidents that resulted in (or could have reasonably resulted in) a catastrophic release of highly hazardous chemicals. Similarly, EPA’s Risk Management Program (RMP) regulations require regulated facilities to conduct incident investigations. In addition, certain management systems, including ISO and Responsible Distribution (National Association of Chemical Distributors) to name just a few, also require RCA.
Whether an organization is subject to PSM, RMP, or management system standards, identifying the root cause of any incident or problem through RCA is a best practice that can significantly benefit organizations by identifying underlying issues to ensure that similar problems do not occur in the future. So, how do you effectively implement RCA?
Six-Step Process
RCA can be broken down into a simple six-step process, as outlined below.
Step 1: Identify and Clearly Describe the Problem
The first step is to understand and document the problem/issue/incident that actually occurred. This might involve interviewing key staff, reviewing security footage, investigating the site, etc. to get an accurate account of the issue. Certainly safety- or security-related incidents might require an immediate fix or prompt action before the carrying out the complete RCA. This is always the first priority.
Some problems are easier to define than others based on what happened and the extent of the issue. When defining and describing the problem, it is important to be as descriptive as possible, as this will aid in future steps to identify the root cause(s).
For example, the first description below is somewhat vague. The second description provides an additional level of detail that more fully documents the situation:
- A forklift driver wasn’t wearing his seatbelt. (vague)
- During a walkthrough of the warehouse on 2/1/20, it was observed that forklift driver John Smith, who is a contract employee, was not wearing his seatbelt while operating the forklift. (clear)
Step 2: Identify Possible Causes…Why?
There are several methods for identifying possible root causes. One of the most common is known as the “5 Why Method”. This approach simply involves asking the question “Why” enough times (i.e., five times) until you get past all the symptoms of a problem and down to the underlying root cause of the issue. The detailed problem description put together during Step 1 serves as the starting point for asking “Why”.
Let’s take our problem description from above a step further to identify the possible causes using the 5 Why Method.
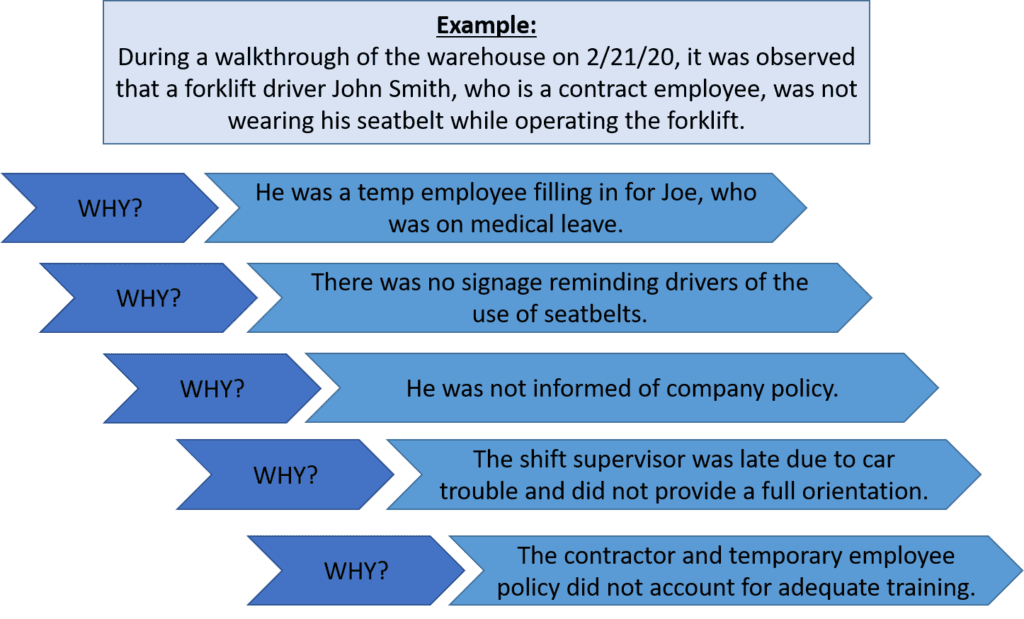 Step 3: Identify Root Cause(s)
Step 3: Identify Root Cause(s)
At this point, the 5 Why Method is leading you to the core issue that set in motion the entire cause-and-effect reaction and, ultimately, that led to the identified problem(s). It’s now time to determine whether the five whys have dug deep enough. Where does your questioning lead you? Is there one root cause or are there a series of root causes contributing to this incident? Often, there are multiple root causes that may be factors to address when preventing future incidents.
In our forklift operator case, the 5 Why Method points to the lack of a standardized checklist of all items to be trained on—including forklift training—prior to a new contract employee coming onsite.
Step 4: Corrective and/or Preventive Action Taken
Based on the identified root causes, it then becomes possible for the facility to determine what corrective and/or prevention actions (CAPAs) can be taken to fix the problem and, just as important, prevent it from occurring in the future. For our example, there are a number of potential CAPAs:
- Stop the employee from operating the forklift and educate him on seatbelt policy prior to resuming work
- Review contract/temp employee training program
- Retrain shift managers on training expectations
- Obtain training records for contract/temp employees
- Provide refresher/retraining, as necessary
- Add signage to forklifts and warehouse bulletin boards about seatbelt policy
Step 5: Analyze Effectiveness
The effectiveness of whatever action is taken in step 4 needs to be evaluated to determine whether it will resolve the root cause. If not, another CAPA should be explored, implemented, and analyzed to assess its impact on the issue/problem. If it is a root cause, it should help to resolve the issue and you should move on to step 6 below.
Let’s return to our example. You might ask, “Was the retraining effective?” An evaluation shows the following:
- Yes, the employee continues to operate the forklift using seatbelt.
- Yes, subsequent walkthroughs of the warehouse over the next six months have not resulted in any additional seatbelt violations.
- The next contract/temp employee brought on to assist during the busy end-of-year season was required to produce current training.
Step 6: Update Procedures, as necessary
As CAPAs are implemented, once they prove effective, related policies and procedures must be updated to reflect any changes made. This step ensures the outcomes of the RCA will be integrated into operations and used to prevent similar incidents from happening in the future.
In our current example, this might mean that the Contractor Policy is updated to include a new section specific to the hiring of contract/temp employees with the following requirements:
- Obtain valid training certificates for work performed
- Ensure Managers conduct on-the-job training for contract/temp employees specific to work performed
Benefits of RCA
Following these six steps will help to ensure a thorough investigation that identifies the root cause(s) versus just symptoms is conducted. It further ensures that any changes related to the root cause are integrated into the organization to prevent similar events from happening again. In the end, the RCA process can help:
- Reduce the risk of injury and/or death to workers and community members
- Reduce the potential for environmental damage
- Avoid unnecessary costs resulting from business interruption; emergency response and cleanup; increased regulation, audits, and inspections; and OSHA or EPA fines
- Improve public trust by maintaining an incident-free record
- More effectively control hazards, improve process reliability, increase revenues, decrease production costs, lower maintenance costs, and lower insurance premiums

Employees Need Rules, Not Regulations
KTL recently announced our partnership with Martin Mantz Compliance Solutions (Martin Mantz), developer of the GEORG Compliance Management System® software. KTL is providing regulatory compliance expertise to the German-based company as it expands its offerings to clients with operations in the United States.
In this recent article, our partners at Martin Mantz discuss how Rudolph Logistics Group, an international logistics service provider from Germany, is using GEORG as a compliance solution to provide employees clear information in accordance with ISO standards on:
- Tasks – what they have to do
- Responsibilities for implementation – who needs to do it
- Date/time of completion – when it needs to be done
- Description of the way the task is to be performed – how the task must be fulfilled
The objective is to simplify requirements to the extent possible so employees can focus on tasks to be completed without needing to interpret complicated and extensive guidelines. Read more…

April 16 Webinar: Improving EHS Management with IT
Effective information management is critical to complying with complex EHS regulations. Join KTL and Southeast Missouri State University (SEMO) for this APPA webinar to get helpful tips for the successful management of EHS information, data, documents, and records.
Improving EHS Management with Information Technology: A University Demonstration
April 16, 2020 | Noon – 1:00 p.m. CT
REGISTER NOW!
This webinar will use a formal EHS management system model (plan-do-check-act) to highlight the importance of:
- Identifying, understanding, and documenting applicable EHS requirements
- Providing easy-to-use EHS information management tools
- Capturing institutional knowledge of experienced staff for operational sustainability
Learning Objectives
Facility managers, plant operators, EHS staff, and supervisors working in higher education will better understand:
- Key components of an effective EHS management system based on ISO 14001/45001
- Best practices for applying information technology to assist with EHS compliance
- Strategies for improving adoption of new technology tools throughout campus
- How to use an affordable, available technology platform (Microsoft SharePoint®) to enhance EHS compliance and communication practices
Presenters
SEMO’s Autumn Gentry will join KTL Principal Joseph Tell to provide a demonstration of SEMO’s recent efforts to manage and communicate EHS information using Microsoft SharePoint® tools to simplify EHS compliance.
About APPA, Leadership in Educational Facilities
Formerly known as the Association of Physical Plant Administrators, APPA is recognized globally as a leader in professional development programs, credentialing, research, publications, networking, and information services for the educational facilities profession. APPA’s mission is to “support educational excellence with quality leadership and professional management through education, research and recognition.”
