
Comments: 1 Comment
5/20/20 Webinar: Intentional Adulteration & Food Defense
The FDA’s Intentional Adulteration Rule is aimed at preventing intentional adulteration from acts intended to cause wide-scale harm to public health, including acts of terrorism targeting the food supply. This is an incredibly important topic for the food industry to understand.
Join Kestrel Tellevate LLC (KTL) Principal Bill Bremer and BSI Americas Director Neil Coole for a free webinar that will provide guidance to keep your company safe and in compliance.
Webinar: Intentional Adulteration & Food Defense
May 20, 2020 | 2:00 – 3:00 p.m. ET
REGISTER NOW!
While there are a number of Food Safety Management Systems available today to prevent accidental contamination, a deliberate attack can often bypass food safety protocols–getting past even the most rigorous systems. Fortunately, there is a “how-to” guide available for the food industry called PAS 96, which is intended to help protect and defend food and drink from deliberate attack.
Learning Objectives
During this webinar, our speakers will highlight the following:
- Introduction to Intentional Adulteration & Food Defense
- Requirements of the FDA Intentional Adulteration Rule
- How to build a Food Defense strategy
- How using PAS 96 will help to reduce the likelihood and impact of a deliberate attack
- How you can get your free downloadable copy of PAS 96, Guidance on Food and Drink Defense
Managing Projects & Permits
How many permits does your operating system (e.g., facilities, production, storage, transportation, distribution) have? What kinds of requirements are associated with each of those permits? Who is responsible for making sure requirements are fulfilled? Are there key/critical dates? How many contractors/vendors do you have carrying out activities pertaining to the many diverse permit requirements? How do you manage all that information? And, importantly, how do you verify compliance?
Depending on the breadth and locations of your operations, managing permits and their associated requirements and due dates without a centralized system in place can be an insurmountable challenge. This was certainly true for a large transportation company managing over 3,600 permits for over 1,600 projects across more than 20 states. Finding a better way to track and manage permits wasn’t just a matter of convenience, it was a necessity.
Web-based Tracking System
After a series of washout incidents, the company’s Engineering Department stepped up its efforts to develop a program to ensure engineering and maintenance activities were meeting applicable construction and environmental permit requirements. With so many activities, responsible parties, and deadlines, the Department retained Kestrel Tellevate LLC (KTL) to develop a web-based project tracking system to help:
- Track permit requirements and construction restriction timeframes
- Produce project-specific All Permits Issued (API) documents
- Track post-activity mitigation requirements
- Manage change information
- Report actual-to-budget performance
While the Engineering Department remains responsible for the permitting activities associated with all construction, maintenance, and emergency response activities, KTL’s Permit Tracking System (PTS) offers a cloud-based project management solution to facilitate permit tracking across a variety of data points.
How It Works
The PTS serves as a communication conduit by providing a standardized approach to project/permit activity tracking, while distributing periodic, tailored reports that allow the Engineering Department to manage project activities, as needed. Integrating with internal databases, PTS provides a means to supplement project data with ongoing contractor/consultant input. This enables comprehensive program oversight on the timeliness of the permitting effort and project details, which, in turn, offers preemptive visibility on issues that may affect project construction and permit compliance.
In short, PTS allows the company to:
- Catalog and track permits in one database
- Document and track project conditions, impacts, construction timeframe restrictions, sensitive resources, etc.
- Send and receive notifications of permits about to expire
- Coordinate and communicate with project contractors
- Establish accountability and a standardized approach for reporting and performance measurement
- Effectively manage project process from permitting through handover to construction
- Monitor financial performance
Business Benefits
The Engineering Department has managed nearly 1,600 projects with more than 3,600 associated permits through PTS. Permits in the system include 404 (most common), 401, Floodplain, NESHAPS, FAA, 402, Air, Coast, Air Emissions, 408 Levee, Coast Guard Bridge, Heritage Tree, Tank, Well, Excavated Materials, NPDES, and others.
With this many projects and permits being managed through a consolidated system, PTS is providing many business benefits, including the following:
- Improved program efficiency, consistency, and coherence by fostering a standardized approach to all permitting data management and input by third-party users
- Customized, automated reporting that allows for enhanced progress monitoring, project accountability, and detailed oversight
- Flexible, cloud-based approach to accommodate a variety of program management aspects into a single tool for real-time, comprehensive visibility
- Sole repository for all project management data to help foster communication and coordination both internally and with contractors/consultants
- Improved permit compliance assurance reliability

Comments: No Comments
GFSI Scheme Provisions to COVID-19 Audit Disruptions
The following information outlines provisions the GFSI-benchmarked schemes are taking to account for audit disruptions due to COVID-19, as of April 21, 2020.
FSSC 22000
Re-Certification Audits (V5 upgrade audits)
- A risk assessment will be completed.
- The decision from the risk assessment could lead to extension to the current V4.1 Certificate of up to 6 months.
- The full V5 re-certification audit will need to take place within 6 months.
- The new V5 certificate will have dates aligned with the current certification cycle.
Surveillance Audits (V5 upgrade audits)
- A risk assessment will be completed.
- The decision from the risk assessment could
lead to:
- Maintaining the current V4.1 Certificate
- Suspending the V4.1 Certificate
- Postponement of the surveillance/periodical V5 upgrade audit by a maximum of 6 months.
BRC GS
Recertification Audit
Where the site is operational, but a physical audit cannot occur on or before the due date and will result in an existing certificate expiring, a certificate extension of up to 6 months validity may be issued based on:
- The successful completion of a risk assessment by the certification body confirming it is appropriate to continue certification.
- The certification body completing a discussion
with the site and review of procedures in place to establish the impact of
COVID-19 extraordinary circumstances to the site operations and the effective
implementation of an emergency response plan.
- Certifications can only be extended by the current certification body.
- Sites with C & D grades may not be extended.
- For BRCGS Packaging, any extended certificates will be against Version 5.
IFS
IFS is subject to the decisions of local authorities and cannot provide a general statement (each situation need to be assessed individually). In the case that an audit cannot be performed on time:
- This will result in the certificate not being renewed.
- An exceptional extension of the existing IFS Certificates is not possible.
Due to precautions taken by local authorities, it may not be possible to carry out audits. In this case, existing IFS certificates remain valid until the end of their term and then lose their regular validity.
IFS appeals to retailers and their suppliers to contact and find bilateral solutions so that supplier contracts can be maintained. The IFS will make it visible in the database if IFS certificates could not be renewed due to COVID-19.
SQF
A certifying body can request to SQF for a site to have a one-time 6-month extension from the certificate expiration date.
- Request may not occur until site is within the audit window of the audit.
- Certifying body will conduct a risk assessment to understand and determine if there is a need to extend the certificate following the IAF Informative Document for Management of Extraordinary Events or Circumstances Affecting ABs, CABs, and Certified Organizations (IAF ID 3:2001).
- Certifying body will submit a change request and Notification Form to SQF for approval.
- Requests will be considered by the SQF Compliance Manager in consultation with the technical team and applicable certifying body and/or legal counsel.
- If the risk assessment identified a low risk of continued certification for a site, SQF will approve and certifying body will extend the expiration date for 6 months from the recertification date.
- Sites that are in the process of switching to a new certifying body, the certifying body that holds the current site’s certificate will be required to conduct the risk assessment to determine the risk level to the existing certificate.
- Unannounced audits can be waived up to 5/31/2020. Any waived must be conducted in 2021.
KTL will continue to track these changes and their impacts on the food industry. We hope KTL can be a trusted resource on many levels now and as we eventually return to “business as usual”.

Getting to the Root Cause
At the most basic level, a root cause is the fundamental reason—or the highest-level cause—for the occurrence of a problem, incident, or event. The root cause sets in motion the entire cause-and-effect reaction that ultimately leads to the problem. Getting to the root cause of any problem is important not just for resolving the issue at hand, but for identifying underlying issues to ensure that similar problems do not occur in the future. This starts with a process called the root cause analysis (RCA).
What Is the Root Cause Analysis (RCA)?
A root cause can be permanently eliminated through process improvement. RCA is a method of problem-solving used to identify the underlying (i.e., root) cause(s) of a problem/incident. RCA can be used to solve problems and provide preventive actions for:
- Major accidents
- Everyday incidents
- Minor near misses
- Human errors
- Maintenance problems
- Medical mistakes
- Productivity issues
- Manufacturing mistakes
- Environmental releases
- Risk analysis, risk mapping
RCA is a systematic process based on the basic idea that effective management requires more than merely putting out fires. RCA focuses on finding a way to prevent these fires from recurring. Rather than just treating symptoms, RCA seeks to identify and address the true, underlying concerns that contribute to a problem or event.
Why is this important? If you just treat the symptoms of the problem, that alleviates them for the short term, but it does nothing to prevent the problem from coming back again. Lasting solutions address the underlying factors—the root cause(s)— that create the problem in the first place. Targeting corrective measures at the identified root causes, subsequently, is the best way to alleviate risk and ensure that similar problems do not occur in the future.
Best Practice
Both the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) encourage organizations to conduct RCA following an incident or near miss at a facility. In fact, facilities covered by OSHA’s Process Safety Management (PSM) standard are required to investigate incidents that resulted in (or could have reasonably resulted in) a catastrophic release of highly hazardous chemicals. Similarly, EPA’s Risk Management Program (RMP) regulations require regulated facilities to conduct incident investigations. In addition, certain management systems, including ISO and Responsible Distribution (National Association of Chemical Distributors) to name just a few, also require RCA.
Whether an organization is subject to PSM, RMP, or management system standards, identifying the root cause of any incident or problem through RCA is a best practice that can significantly benefit organizations by identifying underlying issues to ensure that similar problems do not occur in the future. So, how do you effectively implement RCA?
Six-Step Process
RCA can be broken down into a simple six-step process, as outlined below.
Step 1: Identify and Clearly Describe the Problem
The first step is to understand and document the problem/issue/incident that actually occurred. This might involve interviewing key staff, reviewing security footage, investigating the site, etc. to get an accurate account of the issue. Certainly safety- or security-related incidents might require an immediate fix or prompt action before the carrying out the complete RCA. This is always the first priority.
Some problems are easier to define than others based on what happened and the extent of the issue. When defining and describing the problem, it is important to be as descriptive as possible, as this will aid in future steps to identify the root cause(s).
For example, the first description below is somewhat vague. The second description provides an additional level of detail that more fully documents the situation:
- A forklift driver wasn’t wearing his seatbelt. (vague)
- During a walkthrough of the warehouse on 2/1/20, it was observed that forklift driver John Smith, who is a contract employee, was not wearing his seatbelt while operating the forklift. (clear)
Step 2: Identify Possible Causes…Why?
There are several methods for identifying possible root causes. One of the most common is known as the “5 Why Method”. This approach simply involves asking the question “Why” enough times (i.e., five times) until you get past all the symptoms of a problem and down to the underlying root cause of the issue. The detailed problem description put together during Step 1 serves as the starting point for asking “Why”.
Let’s take our problem description from above a step further to identify the possible causes using the 5 Why Method.
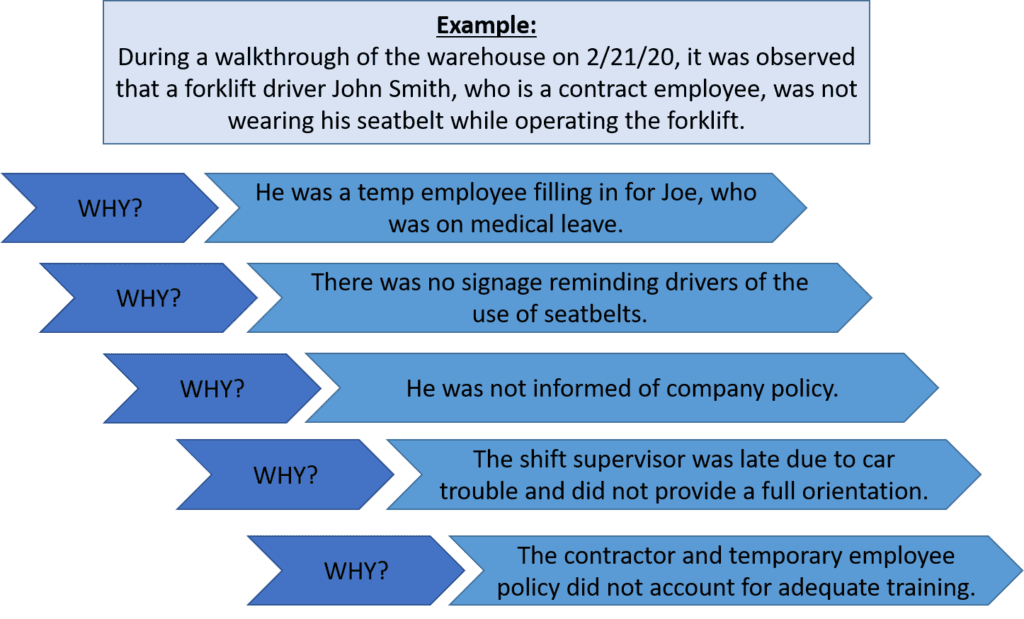 Step 3: Identify Root Cause(s)
Step 3: Identify Root Cause(s)
At this point, the 5 Why Method is leading you to the core issue that set in motion the entire cause-and-effect reaction and, ultimately, that led to the identified problem(s). It’s now time to determine whether the five whys have dug deep enough. Where does your questioning lead you? Is there one root cause or are there a series of root causes contributing to this incident? Often, there are multiple root causes that may be factors to address when preventing future incidents.
In our forklift operator case, the 5 Why Method points to the lack of a standardized checklist of all items to be trained on—including forklift training—prior to a new contract employee coming onsite.
Step 4: Corrective and/or Preventive Action Taken
Based on the identified root causes, it then becomes possible for the facility to determine what corrective and/or prevention actions (CAPAs) can be taken to fix the problem and, just as important, prevent it from occurring in the future. For our example, there are a number of potential CAPAs:
- Stop the employee from operating the forklift and educate him on seatbelt policy prior to resuming work
- Review contract/temp employee training program
- Retrain shift managers on training expectations
- Obtain training records for contract/temp employees
- Provide refresher/retraining, as necessary
- Add signage to forklifts and warehouse bulletin boards about seatbelt policy
Step 5: Analyze Effectiveness
The effectiveness of whatever action is taken in step 4 needs to be evaluated to determine whether it will resolve the root cause. If not, another CAPA should be explored, implemented, and analyzed to assess its impact on the issue/problem. If it is a root cause, it should help to resolve the issue and you should move on to step 6 below.
Let’s return to our example. You might ask, “Was the retraining effective?” An evaluation shows the following:
- Yes, the employee continues to operate the forklift using seatbelt.
- Yes, subsequent walkthroughs of the warehouse over the next six months have not resulted in any additional seatbelt violations.
- The next contract/temp employee brought on to assist during the busy end-of-year season was required to produce current training.
Step 6: Update Procedures, as necessary
As CAPAs are implemented, once they prove effective, related policies and procedures must be updated to reflect any changes made. This step ensures the outcomes of the RCA will be integrated into operations and used to prevent similar incidents from happening in the future.
In our current example, this might mean that the Contractor Policy is updated to include a new section specific to the hiring of contract/temp employees with the following requirements:
- Obtain valid training certificates for work performed
- Ensure Managers conduct on-the-job training for contract/temp employees specific to work performed
Benefits of RCA
Following these six steps will help to ensure a thorough investigation that identifies the root cause(s) versus just symptoms is conducted. It further ensures that any changes related to the root cause are integrated into the organization to prevent similar events from happening again. In the end, the RCA process can help:
- Reduce the risk of injury and/or death to workers and community members
- Reduce the potential for environmental damage
- Avoid unnecessary costs resulting from business interruption; emergency response and cleanup; increased regulation, audits, and inspections; and OSHA or EPA fines
- Improve public trust by maintaining an incident-free record
- More effectively control hazards, improve process reliability, increase revenues, decrease production costs, lower maintenance costs, and lower insurance premiums

Comments: 4 Comments
Apr. 30 Webinar: Maintain Plant Sanitation Following Shutdown
Many food companies face challenges when it comes to sanitation and hygiene, particularly after periods of shutdown or emergency response when the company returns to “business as usual”. Join Kestrel Tellevate LLC (KTL) Principal Bill Bremer and DNV GL for a free webinar that will provide guidance to keep your company safe and in compliance.
Maintain Your Plant, Equipment & Personnel Sanitation Following Shutdown Periods
April 30, 2020 | 10:00 – 11:30 a.m. CT
Register Now!
This webinar will focus on sanitation and hygiene best practices for building, equipment, personnel areas, personnel, and employee welfare as it relates to startup for pre-operations following shutdown or emergency response periods. Each area will be described, along with the related sanitation/hygiene issues, concerns, possible impacts, risks, inspection, observation, and controls.
Learning Objectives
Topics covered in the webinar include the following:
- Various methods of sterilization, sanitation, and disinfection
- Potency in killing germs and unknowns of efficacy
- Applicability in manufacturing, processing, holding, and for various sizes of packaging
- Advantages and disadvantages of inspection types (e.g., visual, odor, physical state)
- Recommendations to achieve effective results with Environmental monitoring (EM) programs
- Considerations for expanded programs based on the re-start situation
- Documenting the sanitation processes
- Responding to unanticipated testing or observations

Employees Need Rules, Not Regulations
KTL recently announced our partnership with Martin Mantz Compliance Solutions (Martin Mantz), developer of the GEORG Compliance Management System® software. KTL is providing regulatory compliance expertise to the German-based company as it expands its offerings to clients with operations in the United States.
In this recent article, our partners at Martin Mantz discuss how Rudolph Logistics Group, an international logistics service provider from Germany, is using GEORG as a compliance solution to provide employees clear information in accordance with ISO standards on:
- Tasks – what they have to do
- Responsibilities for implementation – who needs to do it
- Date/time of completion – when it needs to be done
- Description of the way the task is to be performed – how the task must be fulfilled
The objective is to simplify requirements to the extent possible so employees can focus on tasks to be completed without needing to interpret complicated and extensive guidelines. Read more…

April 16 Webinar: Improving EHS Management with IT
Effective information management is critical to complying with complex EHS regulations. Join KTL and Southeast Missouri State University (SEMO) for this APPA webinar to get helpful tips for the successful management of EHS information, data, documents, and records.
Improving EHS Management with Information Technology: A University Demonstration
April 16, 2020 | Noon – 1:00 p.m. CT
REGISTER NOW!
This webinar will use a formal EHS management system model (plan-do-check-act) to highlight the importance of:
- Identifying, understanding, and documenting applicable EHS requirements
- Providing easy-to-use EHS information management tools
- Capturing institutional knowledge of experienced staff for operational sustainability
Learning Objectives
Facility managers, plant operators, EHS staff, and supervisors working in higher education will better understand:
- Key components of an effective EHS management system based on ISO 14001/45001
- Best practices for applying information technology to assist with EHS compliance
- Strategies for improving adoption of new technology tools throughout campus
- How to use an affordable, available technology platform (Microsoft SharePoint®) to enhance EHS compliance and communication practices
Presenters
SEMO’s Autumn Gentry will join KTL Principal Joseph Tell to provide a demonstration of SEMO’s recent efforts to manage and communicate EHS information using Microsoft SharePoint® tools to simplify EHS compliance.
About APPA, Leadership in Educational Facilities
Formerly known as the Association of Physical Plant Administrators, APPA is recognized globally as a leader in professional development programs, credentialing, research, publications, networking, and information services for the educational facilities profession. APPA’s mission is to “support educational excellence with quality leadership and professional management through education, research and recognition.”

Comments: No Comments
KTL Announces Partnership with German Company Martin Mantz
KTL is pleased to announce our partnership with Martin Mantz Compliance Solutions (Martin Mantz), developer of the GEORG Compliance Management System® software. KTL is providing regulatory compliance expertise to the German-based company as it expands its offerings to clients with operations in the United States.
“Martin Mantz has created something unique with the GEORG software in that it simplifies and provides an interpretation of legal and technical requirements in a customer-specific database,” KTL Principal Lisa Langdon states. “KTL’s understanding of industrial operations, as well as U.S. legal and technical requirements (e.g., EPA, OSHA, FDA, ISO), allows us to translate these requirements into simple tasks in the GEORG system that employees can follow to help fulfill regulatory requirements.”
How GEORG Works
GEORG is used to make the requirements of standards and regulations comprehensible and transparent. KTL specializes in the practical mapping of legal requirements and audits. These audits allow KTL to create technical content for the GEORG system based on facility-specific applicability. We then work directly with the company to delegate the identified tasks. If there are revisions in the standards/regulations, KTL works in the system to ensure tasks are updated to meet regulatory requirements.
The benefits of this approach include:
- Effectiveness – All tasks are assigned, easily formulated, and regularly updated.
- Efficiency – The effort and expertise required to understand complicated regulations is reduced.
- Transparency – Responsibilities are clear and easily visible to all employees.
- Conformity – Compliance status within the system reflects the degree of fulfilment of the related requirements.
Faber-Castell Expands GEORG Implementation to U.S. Subsidiary
Faber-Castell Cosmetics, an internationally renowned Martin Mantz customer with worldwide operations, is already benefitting from the Martin Mantz-KTL partnership. After successful implementation of the GEORG software in their German facilities, Martin Mantz has worked with KTL to expand usage to Faber-Castell’s subsidiary in the U.S.
About Martin Mantz Compliance Solutions
Martin Mantz Compliance Solutions, based in Grosswallstadt and Leipzig, Germany, offers its contractual partners services in the area of legal organization (GEORG) of companies to avoid organizational negligence and compliance violations. This includes consulting and provision of the compliance software GEORG Compliance Management System®, implementation of the technical and legal modules, as well as construction and maintenance of the customer-specific database. https://www.martin-mantz.de/
About Kestrel Tellevate LLC
KTL is a multidisciplinary consulting firm that specializes in providing environmental, health, and safety (EHS) and food safety management and compliance consulting services to private and government clients. Our primary focus is to build strong, long-term client partnerships and provide tailored solutions to address regulatory requirements. KTL’s services include management system development and implementation, auditing and assessments, regulatory compliance assistance, information management solutions, and training. KTL is a Small Business Administration-registered company with headquarters in Madison, WI and Atlanta, GA and offices across the Midwest and Washington, D.C. www.kestreltellevate.com

Comments: No Comments
Managing Aerosol Cans as Universal Waste
Aerosol cans have long provided regulatory challenges under the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Some states have defined aerosol cans as universal waste; some states define it as reactive (D003) waste. On December 9, 2019, the EPA published a new rule (effective February 7, 2020) adding hazardous waste aerosol cans to the Universal Waste Program under the federal Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (RCRA) regulations.
This change provides a clear, protective system for managing discarded aerosol cans. The streamlined universal waste regulations are expected to ease regulatory burdens on retail stores and others that discard hazardous waste aerosol cans; promote the collection and recycling of these cans; and encourage the development of municipal and commercial programs to reduce the quantity of these wastes going to municipal solid waste landfills or combustors.
Current Review of Universal Waste
The designation of universal waste holds several advantages for generators. Universal waste doesn’t “count” against generator status. It does not have to be manifested and generally requires specific labeling language.
Under EPA’s definition, the following are the current universal waste streams:
- Batteries (Li, Ni-Cd, Ag, Hg)
- Mercury-containing equipment (MCE)
- Electric lamps
- Cathode ray tubes (in electronics)
- Pesticides (recalled or farmer-generated)
Adding Aerosol Cans
Adding aerosol cans to the EPA’s Universal Waste Program now provides the option for generators to manage the waste as hazardous or universal. The program addresses emissions with more stringent language and allows generators to set up separate management.
More specifically, the following outlines some basic details of the program for effectively managing aerosol cans as universal waste:
- If the aerosol can is empty (i.e., at ambient pressure, there is no more liquid inside), it is considered an empty container. It can be recycled as metal or thrown away as solid waste (except for Nebraska, where it is D003).
- Full and partial aerosols can be recycled.
- Depending on the vendor, segregation may not be required.
- If the aerosol can is punctured, contents must be captured, and a hazardous waste determination must be performed.
- If the waste from the aerosol can is hazardous, the contents count toward generator accumulation.
- The only benefit to generators occurs if they ship unpunctured cans for recycling.
- If a household hazardous waste (HHW) facility accepts business aerosols and punctures them, the HHW facility becomes a generator.
- All emissions must be captured and managed properly; filters may be hazardous.
Regulatory Review
The new program for managing aerosol cans requires a safety program, education, and written documentation. KTL has the experience and expertise to help you evaluate your waste and to properly manage universal waste. Although not as complex as the requirements for proper hazardous waste management, universal waste has nuances that a generator must be aware of to properly meet the regulatory requirements. KTL can help determine how this new regulation applies and if it can help you minimize your regulatory burden, save some money, and manage your waste more efficiently.

Comments: No Comments
Food Intentional Adulteration: Vulnerability Assessment Training
Food Intentional Adulteration:
Vulnerability Assessment Training
April 21, 2020 | 8:30 am – 5:00 pm
Courtyard by Marriott – Chicago O’Hare
2950 S. River Road | Des Plaines, IL
Cost: $500
REGISTER NOW!
Background
On July, 26 2016, the final rule for Mitigation Strategies to Protect Food Against Intentional Adulteration was released as part of the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA). This rule defines the requirements for facilities manufacturing, processing, handling, packing, and storing food products to protect food against acts intended to cause wide-scale public harm to consumers.
The regulation requires all facilities handling food products to complete a vulnerability assessment for their processes. Based on results, facilities are then required to implement mitigation strategies against potential threats (e.g., terrorism, tampering, sabotage).
Training
Kestrel Tellevate LLC’s (KTL) Intentional Adulteration Vulnerability Assessment Training is a one-day course designed to train responsible Food Defense Qualified Individuals to understand the current requirements to protect against intentional adulteration.
This course will focus on the the vulnerability assessment approach, according to the FSMA regulation. The Food Defense Qualified Individual will learn strategies to:
- Implement the Food Defense Plan
- Perform the vulnerability assessment
- Define mitigation strategies
- Conduct periodic review of the Food Defense Plan
Participation in this course will help to ensure compliance with the requirements outlined in the Intentional Adulteration Rule to protect against food adulteration.
 Trainer
Trainer
KTL is pleased to welcome CSQA Foreign Affairs Manager Carlo Merlo as our instructor for this course. Carlo is a Lead Instructor for Intentional Adulteration Vulnerability Assessment.
