Tech Corner: Laboratory Information Management System
Functionality: What does it do?
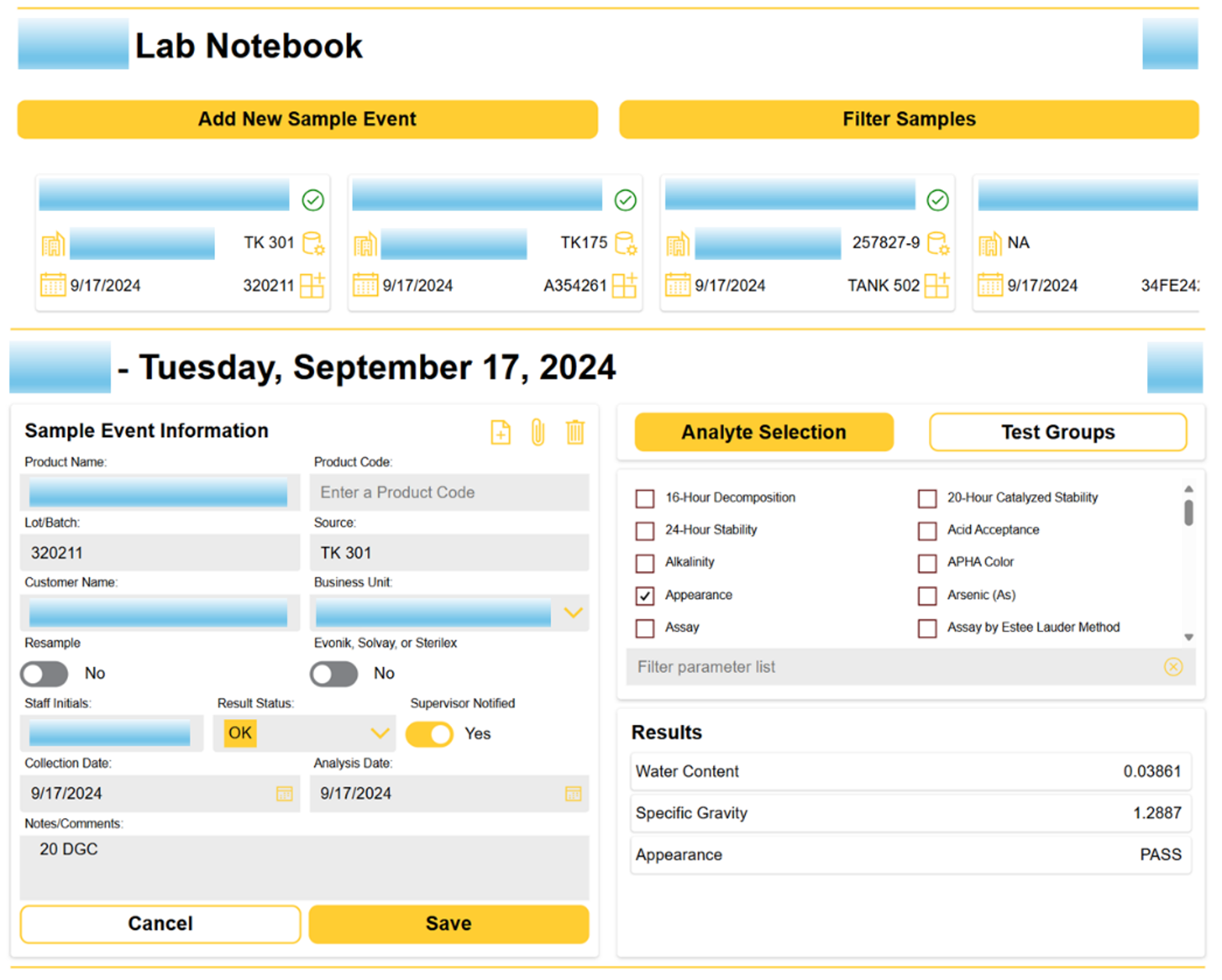
Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS) are tools designed to manage laboratory samples, associated data, and workflows in a user-friendly interface. KTL uses the Microsoft Power Platform to build and customize LIMS to provide organization-specific functionality, including the following:
- Samples can be tracked as individual or grouped assays.
- Workflows can be established to improve processing and reduce errors.
- Data is centralized for access and quality control improvements.
Benefits: Why do you need it?
Having a reliable LIMS can help organizations to:
- Manage and control large amount of laboratory data and samples.
- Reduce time required to track samples.
- Create detailed chain of custody.
- Provide notifications and tracking of approvals.
- Attach documents and photos to samples to provide more detailed information.
- Deliver results to identified users.
Technology Used
- SharePoint or Dataverse
- Power Apps
- Power Automate

Tech Corner: Reminders and Notifications Tool
Functionality: What does it do?
Virtually every regulatory agency (e.g., EPA, OSHA, FDA, USDA) and voluntary certification standard (e.g., ISO, GFSI, organic) has compliance requirements that call for companies to fulfill compliance activities by established deadlines. KTL’s Reminders and Notifications Tool is designed to help organizations make sure these deadlines are not missed. The tool allows users to receive notifications and reminders via email, Microsoft Teams, or other messaging app that action is needed, including the following triggers:
- Document submissions
- Survey/list submissions
- Permit renewals
- Assignment due date is approaching/past due
- Item or document is awaiting approval
- Many, many others
Benefits: Why do you need it?
The Reminders and Notifications Tool helps organizations to:
- Keep multi-step processes moving forward quickly and efficiently.
- More efficiently manage compliance deadlines.
- Remind assigned staff of easy-to-forget due dates.
- Share information and reports with notifications to disseminate key information regularly.
Technology Used
- SharePoint
- Power Automate
- Email, MS Teams, or other communication platform

Tech Corner: Property Management Tool
Functionality: What does it do?
As an organization operates more sites/facilities/properties, the need for a reliable tool to manage them becomes more critical. KTL’s Property Management Tool is designed to help users manage and organize property-related documents and information (e.g., contracts, permits, maps, insurance, other legal information) more efficiently. The tool allows users to:
- Maintain detailed information for each property, including property name, address, county, previous owner, date added, insurance carrier, and description.
- Search for properties using a search bar or by selecting alphabetic filters. Once a property is selected, detailed information about the property (as described above) is displayed.
- Associate related documents to each property. This may include contracts, maps, permits, and other legal documents. Each document entry shows the property name, modification date, document type, and document library location.
- Easily navigate between properties, refresh the view, open comment logs, and select properties for further actions.
Benefits: Why do you need it?
KTL’s Property Management App provides the following:
- Enhanced efficiency: Streamlines property management tasks, reducing the time and effort required to access and manage property information.
- Centralized documentation: Keeps all property-related documents in one place, simplifying retrieval and reducing the likelihood of misfiled documents.
- Improved decision-making: Provides immediate access to comprehensive property details, aiding in quicker and more informed decision-making.
- Scalability: Adapts to growing organizational needs and expanding property portfolios.
Technology Used
- Power Apps: Utilizes Microsoft Power Apps to create a flexible and scalable application that integrates seamlessly with other Microsoft services.
- SharePoint: Leverages Microsoft’s robust cloud infrastructure for secure data storage and efficient data management.

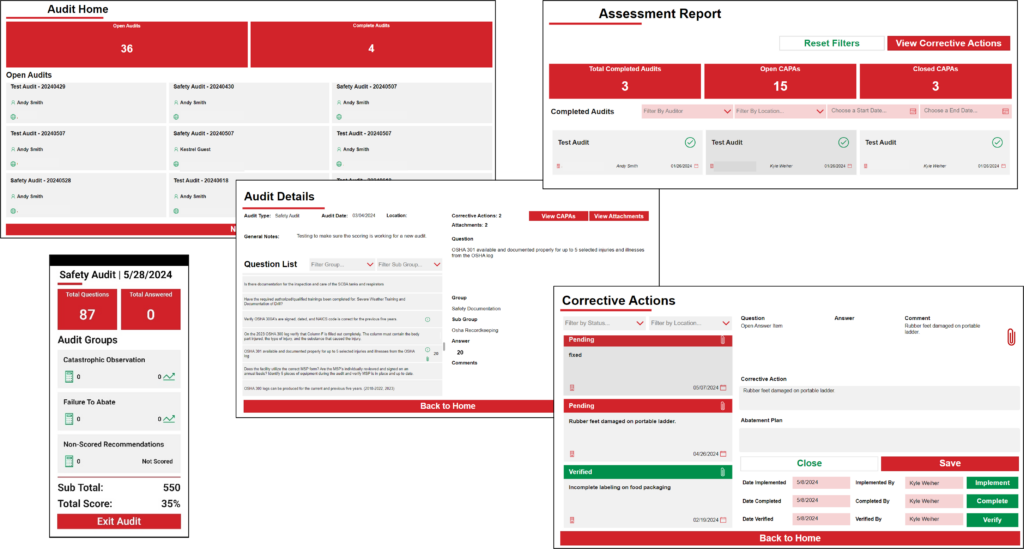
Tech Corner: Audit Tool
Functionality: What does it do?
Audits provide an essential tool for improving and verifying compliance performance. Audits may be used to capture regulatory compliance status (e.g., EPA, FDA, USDA, OSHA); certification system conformance (e.g., ISO, GFSI); and adequacy of internal controls, potential risks, and best practices. KTL’s Audit Tool allows organizations to conduct and manage audits. The interface provides a clear overview of completed audits, displays open and closed corrective and preventive actions (CAPAs), and enables detailed filtering to streamline the management process.
Benefits: Why do you need it?
KTL’s Audit Tool allows users to capture regulatory compliance status and certification system conformance. It ensures that audit processes are tailored and responsive by allowing the user to:
- Add new locations and active users; create and modify assessment types; and adjust question templates, scoring values, and answer options.
- Create custom audit templates by selecting the questions to be included in each audit.
- Track audit progress/completion status by subject.
- Quickly gauge the volume of completed assessments and the number of CAPAs that have been successfully resolved and closed.
Technology Used
- Dataverse
- Power Apps

Tech Corner: Document Approval Process
Functionality: What does it do?
The documents an organization works with are subject to various internal policies, industry standards, compliance requirements, and more. As such, they often require review and approval by various stakeholders at various stages of development. A document approval process uses workflows to streamline and standardize document approvals. KTL’s approval process is set up to automatically route documents, assign review tasks, track progress, and send reminders and notifications when needed. It takes documents from development through final approval, ensuring documents are reviewed at the appropriate time by the appropriate party.
Benefits: Why do you need it?
KTL’s document approval process provides the following:
- Document standardization.
- Streamlined approach for approving and completing tasks involving documents.
- Improved document integrity and accuracy with less opportunity for human error.
- Business efficiencies from automated and streamlined document handling practices.
- Version control and history to create a reliable audit trail.
- Improved access/security for sensitive documents.
Technology Used
- Microsoft SharePoint
- Microsoft Power Automate

Tech Corner: GHG Inventory and Reporting Tool
Functionality: What does it do?
According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), a greenhouse gas (GHG) inventory is a list of emission sources with the associated emissions quantified using standardized methods. KTL’s GHG inventory and reporting tool helps to organize energy use and GHG information and responsibilities. The tool factors in all fuel sources across an organization, including direct (from the facility), direct mobile, and indirect facility combustion, as well as hours worked so that all calculations can be normalized. The tool has built-in conversion factors for reported figures (so facilities report data in their original units) to metric tons of CO2e emitted, allowing the organization to track and understand GHG emissions across the organization.
Benefits: Why do you need it?
KTL’s GHG inventory and reporting tool helps organizations to:
- Collect, track, and manage GHG emission source data and emission trends over time.
- Identify GHG and energy usage reduction opportunities and manage related risks.
- Establish the GHG tracking and documentation that is essential to comply with voluntary GHG programs or mandatory GHG reporting requirements, including the new SEC climate-related disclosure requirements.
- Measure progress towards local, regional, state, federal, and international climate goals.
- Create a baseline of GHG data to inform the development of Climate Action Plans.
- Evaluate the impacts of potential plant renovations, production changes, etc. on emissions.
Technology Used
- Microsoft SharePoint
- Microsoft Power Platform

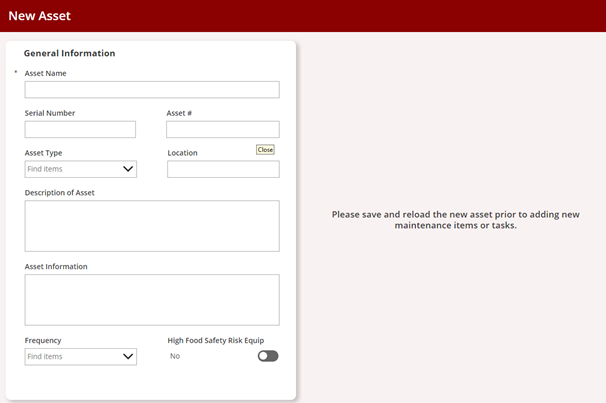
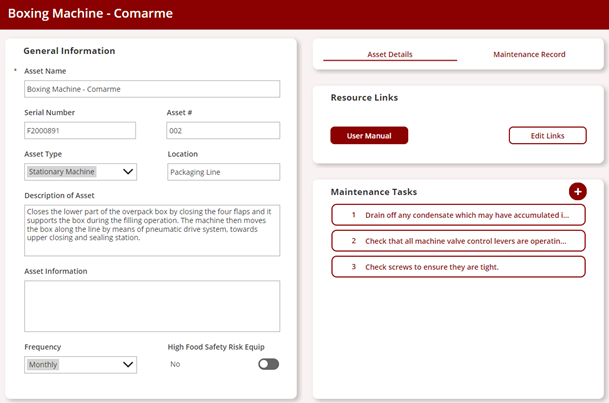
Tech Corner: Asset Management Tool
Functionality: What does it do?
Asset management tools are designed to track, monitor, and manage physical assets while ensuring adherence to regulatory standards and industry requirements. The tools centralize asset data, documentation, and asset-related compliance processes, while reducing the risk of non-compliance.
Benefits: Why do you need it?
- Compliance: Track compliance requirements and maintain auditable records.
- Documentation: Associate assets with manufacturers’ manuals and other required documentation.
- History: Record details of past maintenance and repairs.
- Location: Track the location of the asset and the department or users that it is assigned to.
- Maintenance: Track and schedule maintenance tasks.
- Properties: Maintain a fully customizable list of details about many different types of assets.
Technology Used
- SharePoint
- Power Apps
- Power Automate

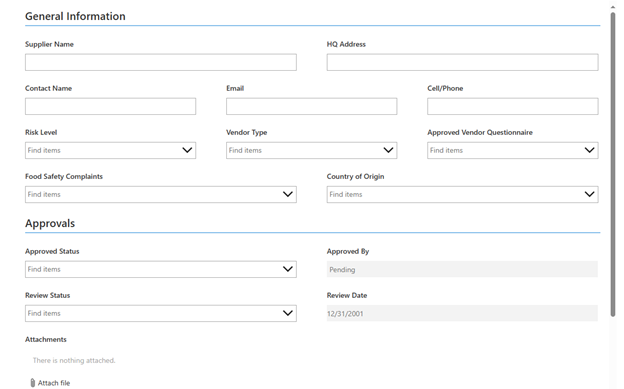
Tech Corner: Vendor Management
Functionality: What does it do?
Vendor management is the process of coordinating vendors and suppliers. It includes activities such as selecting and approving suppliers, reviewing qualifications, negotiating contracts, ensuring quality, and compiling required documentation. KTL’s vendor management/supplier approval system provides a web-based tool to effectively approve and manage vendors and suppliers. It enables businesses to control costs, minimize potential risks related to vendors/suppliers, and meet regulatory requirements (e.g., Food Safety Modernization Action (FSMA) Foreign Supplier Verification Program (FSVP) Rule).
Benefits: Why do you need it?
KTL’s web-based supplier approval system:
- Provides a checklist to ensure all vendors and suppliers meet required criteria (e.g., certifications, licenses, performance history).
- Manages vendor and supplier-specific requirements.
- Stores and organizes supplier documents and records; suppliers can upload their own documents in a secure folder (if external user access is allowed).
- Enables facilities to conduct and manage vendor evaluations.
- Sends email notifications of supplier-related compliance deadlines.
Technology Used
- SharePoint
- Power Automate (for email notifications)

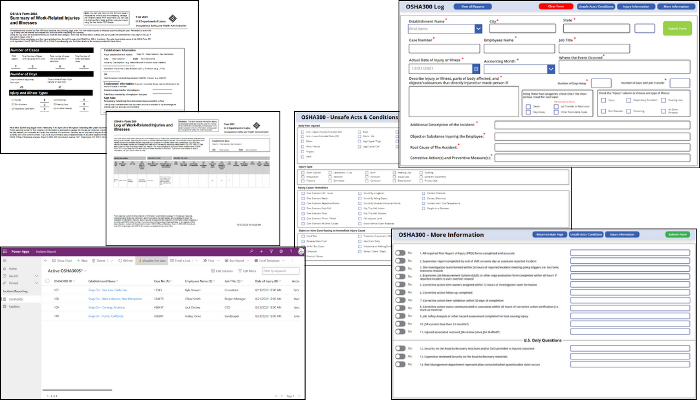
Tech Corner: OSHA 300 Log Management
Functionality: What does it do?
The Occupational Safety and Health (OSH) Act requires certain employers to prepare and maintain records of work-related injuries and illnesses. Employers must keep an OSHA 300 Log and OSHA 300A Summary for each establishment or site that documents specific details when an incident occurs. KTL’s OSHA 300 PowerApp is a comprehensive intake form tailored to OSHA 300 and OSHA 300A requirements that makes it easier to collect, search, and analyze data—and maintain OSHA compliance.
Benefits: Why do you need it?
KTL’s OSHA 300 PowerApp provides the following:
- Easier data entry. The app guides users through all required OSHA questions to help ensure no crucial data points are missed.
- Reduced errors. The intuitive design and in-built checks reduce the chances of errors, leading to more accurate reporting.
- Improved searchability. Microsoft Dataverse provides quick and efficient access to stored records. The digital format makes it easy to filter, search, and analyze records and data to offer deeper insights into safety performance.
- Mobility. The PowerApp can be accessed from any device, anytime, anywhere, making the reporting process more flexible.
- Data security. Log entries are stored safely, ensuring data integrity and security.
- Improved visualization. Incident data can be viewed in real-time as two paginated reports:
- OSHA 300 Log: Detailed record of work-related injuries and illnesses.
- OSHA 300A: Summary of the OSHA 300 Log, which can be displayed prominently at workplaces.
Technology Used
- PowerApps
- Microsoft Dataverse
- Power BI

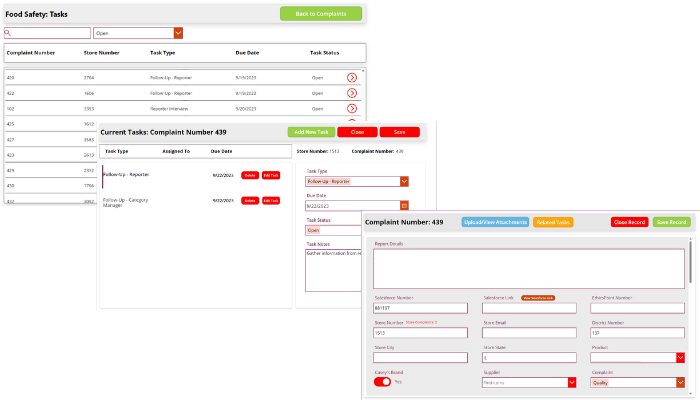
Tech Corner: Customer Complaints Log
Functionality: What does it do?
Whether a company sells directly to consumers or to other manufacturers, managing, monitoring, responding to, and trending customer complaints is an important part of a risk management strategy. KTL’s customer complaints log provides a central location for companies to capture and respond to customer complaints—and then trend that data to ensure complaints are tracked to closure and any necessary changes are made to alleviate company risk.
Benefits: Why do you need it?
A web-based customer complaints log:
- Simplifies collection of customer complaint information via electronic forms.
- Aggregates all customer complaints in one central database to support the management and trending of customer complaint data.
- Documents, assigns, and tracks resolution of customer complaints.
- Establishes follow-up action requirements and associated deadlines to ensure any required changes are made.
- Helps manage the risks associated with customer complaints and potential recalls.
- Meets certification standard requirements for complaint management (e.g., Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI)).
Technology Used
- Power Apps: Creates customized forms and applications for data capture and initial complaint logging.
- Power BI: Allows for advanced analytics, data visualization, and trending of customer complaint data.
- Power Automate: Automates the workflow, task assignments, reminders, and follow-up actions related to complaints.